Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In an experiment on the specific heat of a metal, a 0.20 kg block of the metal at 150 °C is dropped in a copper calorimeter (of water equivalent 0.025 kg) containing 150 cm3 of water at 27 °C. The final temperature is 40 °C. Compute the specific heat of the metal. If heat losses to the surroundings are not negligible, is your answer greater or smaller than the actual value for the specific heat of the metal?
उत्तर १
Mass of the metal, m = 0.20 kg = 200 g
Initial temperature of the metal, T1 = 150°C
Final temperature of the metal, T2 = 40°C
Calorimeter has water equivalent of mass, m’ = 0.025 kg = 25 g
Volume of water, V = 150 cm3
Mass (M) of water at temperature T = 27°C:
150 × 1 = 150 g
Fall in the temperature of the metal:
ΔT = T1 – T2 = 150 – 40 = 110°C
Specific heat of water, Cw = 4.186 J/g/°K
Specific heat of the metal = C
Heat lost by the metal, θ = mCΔT … (i)
Rise in the temperature of the water and calorimeter system:
ΔT′’ = 40 – 27 = 13°C
Heat gained by the water and calorimeter system:
Δθ′′ = m1 CwΔT’
= (M + m′) Cw ΔT’ … (ii)
Heat lost by the metal = Heat gained by the water and colorimeter system
mCΔT = (M + m’) Cw ΔT’
200 × C × 110 = (150 + 25) × 4.186 × 13
`:. C = (175xx4.186xx13)/(110xx200) = 0.43 J g^(-1) K^(-1)`
If some heat is lost to the surroundings, then the value of C will be smaller than the actual value.
उत्तर २
Mass of metal block, m = 0.20 kg = 200 g
Fall in the temperature of metal block,
ΔT = (150 – 40) °C = 110 °C
If C be the specific heat of metal, then heat lost by the metal block = 200 x C x 110 cal Volume of water = 150 cm3
mass of water = 150 g
Increase in temperature of water = (40 – 27) °C = 13°C
Heat gained by water = 150 x 13 cal Water equivalent of calorimeter, w = 0.025 kg = 25g
Heat gained by calorimeter, `"w x increase in temperature of calorimeter"`
= 25 x 13 cal
Heat lost by metal block = Heat gained by water + Heat gained by calorimeter
200 x C x 110 = (150 + 25 ) 13
`C = (175xx13)/(200xx100) = 0.1 Cal g^(-1) ""^@C^(-1) = 0.43 J g^(-1) K^(-1)`
if heat is lost to the surroundings, C will be smaller then the actual value
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A child running a temperature of 101°F is given an antipyrin (i.e. a medicine that lowers fever) which causes an increase in the rate of evaporation of sweat from his body. If the fever is brought down to 98 °F in 20 min, what is the average rate of extra evaporation caused, by the drug? Assume the evaporation mechanism to be the only way by which heat is lost. The mass of the child is 30 kg. The specific heat of human body is approximately the same as that of water, and latent heat of evaporation of water at that temperature is about 580 cal g–1.
The coolant in a chemical or a nuclear plant (i.e., the liquid used to prevent the different parts of a plant from getting too hot) should have high specific heat.
A refrigerator converts 100 g of water at 20°C to ice at -10°C in 35 minutes. Calculate the average rate of heat extraction in terms of watts.
Given: Specific heat capacity of ice = 2.1 J g-1°C-1
Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1°C-1
Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J g-1
Water is used in hot water bottles for fomentation. Give a reason.
Find the time taken by a 500 W heater to raise the temperature of 50 kg of material of specific heat capacity 960 J kg-1K-1, from 18°C to 38° C. Assume that all the heat energy supplied by the heater is given to the material.
Give three reasons for the increase of green house gases.
What is meant by global warming?
Without green house effect, the average temperature of earth’s surface would have been:
(a) – 18℃
(b) 33℃
(c) 0℃
(d) 15℃
A substance is heated at a constant rate from a low temperature to a high temperature. A graph of temperature against time is shown in the figure. Which part or parts of the graph correspond(s) to the substance existing in two states?
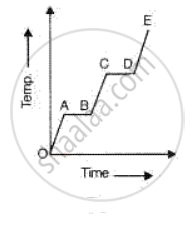
What is heat? What is the S. I. unit of heat?
Specific heat capacity of substance A is 3.8 J g-1 K-1whereas the specific heat capacity of substance B is 0.4 J g-1 K-1. Which of the two is a good conductor of heat? How is one led to this conclusion?
Give two reasons as to why copper is preferred over other metals for making calorimeters.
An electric immersion heater is rated 1250 W. Calculate the time in which it will heat 20 kg of water at 5°C to 65°C.
Write the name.
The amount of heat absorbed at constant temperature by unit mass of a liquid to convert into gaseous phase.
Write a short note.
Specific heat capacity
Why is water used as a coolant in radiators of a car?
The molar specific heats of an ideal gas at constant pressure and volume are denoted by Cp and Cv, respectively. If `gamma = "C"_"p"/"C"_"v"` and R is the universal gas constant, then Cv is equal to ______.
Specific heat capacity of a substance X is 1900 Jkg-1°C-1 means ______.
Two blocks P and Q of different metals having their mass in the ratio 2 : 1 are given same amount of heat. Their temperature rises by same amount. Compare their specific heat capacities.
