Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the name.
The amount of heat absorbed at constant temperature by unit mass of a liquid to convert into gaseous phase.
उत्तर
The amount of heat absorbed at constant temperature by unit mass of a liquid to convert into gaseous phase- Specific latent heat of vaporisation
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A solid of mass 50 g at 150 °C is placed in 100 g of water at 11 °C when the final temperature recorded is 20 °C. Find the specific heat capacity of the solid. (specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J/g °C)
A refrigerator converts 100 g of water at 20°C to ice at -10°C in 35 minutes. Calculate the average rate of heat extraction in terms of watts.
Given: Specific heat capacity of ice = 2.1 J g-1°C-1
Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1°C-1
Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J g-1
A solid metal weighing 150 g melts at its melting point of 800 °C by providing heat at the rate of 100 W. The time taken for it to completely melt at the same temperature is 4 min. What is the specific latent heat of fusion of the metal?
During the phase change does the average kinetic energy of the molecules of the substance increase?
Name three fossil fuels that emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere ?
Study the following procedure and answer the questions below:
1. Take 3 spheres of iron, copper and lead of equal mass.
2. Put all the 3 spheres in boiling water in a beaker for some time.
3. Take 3 spheres out of the water. Put them immediately on a thick slab of wax.
4. Note, the depth that each sphere goes into the wax.
i) Which property of substance can be studied with this procedure?
ii) Describe that property in minimum words.
iii) Explain the rule of heat exchange with this property.
Indian style of cooling drinking water is to keep it in a pitcher having porous walls. Water comes to the outer surface very slowly and evaporates. Most of energy needed for evaporation is taken from the water itself and the water is cooled down. Assume that a pitcher contains 10 kg of water and 0.2 g of water comes out per second. Assuming no backward heat transfer from the atmosphere to the water, calculate the time in which the temperature decrease by 5°C. Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg−1 °C−1 and latent heat of vaporization of water = 2.27 × 106 J kg−1.
Explain, why temperature in hot summer, falls sharply after a sharp shower?
Derive Mayer’s relation.
How much heat energy is necessary to raise the temperature of 5 kg of water from 20°C to 100°C?
Explain why the specific heat capacity at constant pressure is greater than the specific heat capacity at constant volume.
50 g of copper is heated to increase its temperature by 10° C. If the same quantity of heat is given to 5 g water, the rise in its temperature is [Specific heat of copper = 420 joule-kg-1 °C-1 , specific heat of water = 4200 joule-kg-I °C-1]
For a gas `"R"/"C"_"v" = 0.4,` where 'R' is the universal gas constant and 'Cv' is molar specific heat at constant volume. The gas is made up of molecules which are ______.
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for 200 g of water. The heat is extracted at the rate of 100 Js-1. Answer the questions that follow:
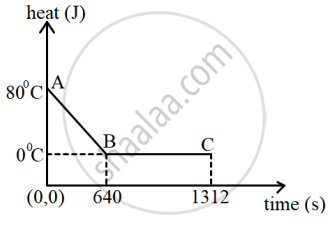
- Calculate specific heat capacity of water.
- Heat released in the region BC.
Which of the following substances (A, B and C) has the highest specific heat?

Specific heat capacity of a substance X is 1900 Jkg-1°C-1 means ______.
Give one example where high specific heat capacity of water is used as heat reservoir.
