Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the given figure ABCD is a rectangle. It consists of a circle and two semi-circles each of
which are of radius 5 cm. Find the area of the shaded region. Give your answer correct to
three significant figures

उत्तर
Length of a rectangle = Radius of two semi-circles Diameter of a circle
= 5 + 5 + 10
= 20 cm
Breadth of a rectangle = Diameter of a circle = 2 x 5 = 10 cm
∴ Area of a rectangle = Length x Breadth
= 20 x 10
= 200 sq. cm
Area of circle = `22/7 xx 5 xx 5` = 78.571 sq.cm
And, area of two semi-circles each of radius 5 cm = `2(1/2 xx 78.571)` = 78.571 sq. cm
Now,
Area of shaded region = Area of a rectangle - Area of a circle - Area of two semi- circle
= 200 - 78.571 - 78.571
= 200 - 157.142
= 42.858 sq.cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
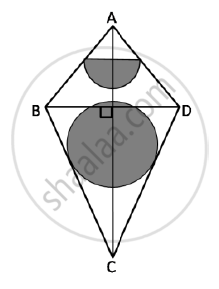
The given figure represents a kite with a circular and a semicircular motifs stuck on it.
The radius of a circle is 2.5 cm and the semicircle is 2 cm. If diagonals AC and BD are
of lengths 12 cm and 8 cm respectively, find the area of the:
1) Shaded part. Give your answer correct to the nearest whole number.
2) Unshaded part
A straight line passes through the points P(–1, 4) and Q(5, –2). It intersects the co-ordinate axes at points A and B. M is the mid-point of the segment AB. Find:
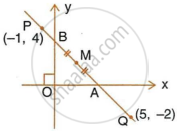
- The equation of the line.
- The co-ordinates of A and B.
- The co-ordinates of M.
(1, 5) and (–3, –1) are the co-ordinates of vertices A and C respectively of rhombus ABCD. Find the equations of the diagonals AC and BD.
Show that A(3, 2), B(6, −2) and C(2, −5) can be the vertices of a square.
- Find the co-ordinates of its fourth vertex D, if ABCD is a square.
- Without using the co-ordinates of vertex D, find the equation of side AD of the square and also the equation of diagonal BD.
O(0, 0), A(3, 5) and B(−5, −3) are the vertices of triangle OAB. Find the equation of median of triangle OAB through vertex O.
O(0, 0), A(3, 5) and B(−5, −3) are the vertices of triangle OAB. Find the equation of altitude of triangle OAB through vertex B.
Point A and B have co-ordinates (7, −3) and (1, 9) respectively. Find:
- the slope of AB.
- the equation of perpendicular bisector of the line segment AB.
- the value of ‘p’ of (−2, p) lies on it.
Use a graph sheet for this question.
Take 1 cm = 1 unit along both x and y axis.
(i) Plot the following points:
A(0,5), B(3,0), C(1,0) and D(1,–5)
(ii) Reflect the points B, C and D on the y axis and name them as B',C'andD' respectively.
(iii) Write down the coordinates of B',C 'and D'
(iv) Join the point A, B, C, D, D ', C ', B', A in order and give a name to the closed figure ABCDD'C'B
A line is of length 10 units and one end is at the point (2, – 3). If the abscissa of the other end be 10, prove that its ordinate must be 3 or – 9.
