Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the circuit shown below, calculate the equivalent resistance between the points (i) A and B, (ii) C and D.
उत्तर

(i) Between the points A and B : Three resistance 2 Ω, 2Ω, 2Ω are in series.
The equivalent resistance R' = 2 + 2 + 2 = 6 Ω
This is joined in parallel with a resistance 2Ω
The equivalent resistance R = `(2 xx 6)/(2 + 6) = 12/8 = 15. Omega`
(ii) Between the points C and D:
The above combination of equivalent resistance 1.5 Ω is in series with two resistances 2Ω and 2Ω
Total effective resistance between the points C and D is R
= 1.5 + 2 + 2 = 5.5
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the expression for resistors connected in series.
The diagram below shows part of a circuit:
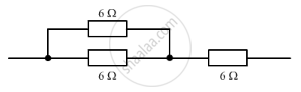
If this arrangement of three resistors was to be replaced by a single resistor, its resistance should be:
(a) 9 Ω
(b) 4 Ω
(c) 6 Ω
(d) 18 Ω
Name a substance of which the resistance remains almost unchanged by the increase in temperature.
A given metallic wire of resistance R is doubled on itself. What will be its new resistance?
What material is used for making wire to prepare heating coils? Give a reason.
Calculate the equivalent resistance between P and Q from the following diagram:
Six resistances are connected together as shown in the figure. Calculate the equivalent resistance between points A and B.

Two resistors of 4Ω and 6Ω are connected in parallel to a cell to draw 0.5 A current from the cell.
Draw a labelled circuit diagram showing the above arrangement.
With the help of a circuit diagram derive the formula for the resultant resistance of three resistances connected:
- in series and
- in parallel
If the current I through a resistor is increased by 100% (assume that temperature remains unchanged), the increase in power dissipated will be:
