Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Magnetic meridian is
पर्याय
a point
a line along north-south
a horizontal plane
a vertical plane
उत्तर
a vertical plane
Magnetic meridian at a place is not a line but a vertical plane passing through the axis of a freely suspended magnet.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State how magnetic susceptibility is different for the three types of magnetic materials, i.e. diamagnetic, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials
What are permanent magnets? Give one example ?
A dip circle is taken to geomagnetic equator. The needle is allowed to move in a vertical plane perpendicular to the magnetic meridian. The needle will stay ______.
Which of the following four graphs may best represent the current-deflection relation in a tangent galvanometer?
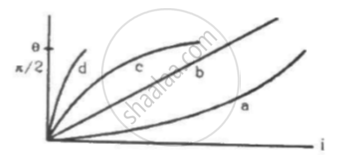
A tangent galvanometer is connected directly to an ideal battery. If the number of turns in the coil is doubled the deflection will
A very long bar magnet is placed with its north pole coinciding with the centre of a circular loop carrying as electric current i. The magnetic field due to the magnet at a point on the periphery of the wire is B. The radius of the loop is a. The force on the wire is
Two long bare magnets are placed with their axes coinciding in such a way that the north pole of the first magnet is 2.0 cm from the south pole of the second. If both the magnets have a pole strength of 10 Am, find the force exerted by one magnet of the other.
Show that the magnetic field at a point due to a magnetic dipole is perpendicular to the magnetic axis if the line joining the point with the centre of the dipole makes an angle of `tan^-1(sqrt 2)` with the magnetic axis
Do permeability and relative permeability have the same dimensions?
The magnetic moment of the assumed dipole at the earth's centre is 8.0 × 1022 A m2. Calculate the magnetic field B at the geomagnetic poles of the earth. Radius of the earth is 6400 km.
The magnetic field due to the earth has a horizontal component of 26 μT at a place where the dip is 60°. Find the vertical component and the magnitude of the field.
A short magnet produces a deflection of 37° in a deflection magnetometer in Tan-A position when placed at a separation of 10 cm from the needle. Find the ratio of the magnetic moment of the magnet to the earth's horizontal magnetic field.
A deflection magnetometer is placed with its arms in north-south direction. How and where should a short magnet having M/BH = 40 A m2 T−1 be placed so that the needle can stay in any position?
A short magnet oscillates in an oscillation magnetometer with a time period of 0.10 s where the earth's horizontal magnetic field is 24 μT. A downward current of 18 A is established in a vertical wire placed 20 cm east of the magnet. Find the new time period.
A bar magnet makes 40 oscillations per minute in an oscillation magnetometer. An identical magnet is demagnetized completely and is placed over the magnet in the magnetometer. Find the time taken for 40 oscillations by this combination. Neglect any induced magnetism.
Answer in brief.
Explain one application of electromagnet.
In a permanent magnet at room temperature ______.
Which of the following is most suitable for the core of an electromagnet?
