Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer in brief.
Explain one application of electromagnet.
उत्तर
Electromagnets are used for various purposes on a day to day basis. For example, electromagnets are used in the large cranes which are used in waste yards. Electromagnets are also widely used in numerous electromechanical and electronic devices. Some of the common uses are given below.
- Uses in Home Appliances: Most of the electric appliances used in the home use electromagnetism as the basic working principle. Some electromagnet uses in the home include the electric fan, electric doorbell, induction cooker, magnetic locks, etc. In an electric fan, the electromagnetic induction keeps the motor rotating on and on making the blade of the fan to rotate. Also in an electric doorbell when the button is pressed, due to the electromagnetic forces the coil gets energized and the bell sounds.
- Uses in Medical Field: The uses of electromagnets are also seen in the medical field. MRI scan which is short for Magnetic Resonance Imaging is a device that uses electromagnets. The device can scan all the tiny details in the human body with the help of electromagnetism.
-
Uses in Memory Storage Devices and Computer Hardware: The data in ebook gadgets and phones are stored in the electromagnetic format in the form of bytes and bits. The computer hardware is also having a magnetic tape which works on the principle of electromagnetism. Even in the olden days’ electromagnets had a huge role in the data storage of VCP and VCR.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State any two advantages of electromagnets over permanent magnets.
Why is the core of an electromagnet made of ferromagnetic materials?
Can we have a single north pole, or a single south pole?
The force on a north pole, `vecF = mvecB` , parallel to the field `vecB` . Does it contradict our earlier knowledge that a magnetic field can exert forces only perpendicular to itself?
Magnetic scalar potential is defined as `U(vec r_2) - U(vec r_1) = - ∫_vec(r_1)^vec(r_2)` `vec (B) . dvec(l)`
Apply this equation to a closed curve enclosing a long straight wire. The RHS of the above equation is then `-u_0 i` by Ampere's law. We see that `U(vec(r_2)) ≠ U(vec(r_1))` even when `vec r_2 =vec r_1` .Can we have a magnetic scalar potential in this case?
Magnetic meridian is
A dip circle is taken to geomagnetic equator. The needle is allowed to move in a vertical plane perpendicular to the magnetic meridian. The needle will stay ______.
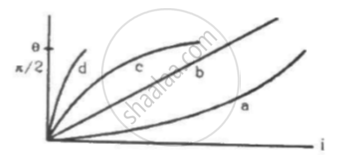
Which of the following four graphs may best represent the current-deflection relation in a tangent galvanometer?
Two long bare magnets are placed with their axes coinciding in such a way that the north pole of the first magnet is 2.0 cm from the south pole of the second. If both the magnets have a pole strength of 10 Am, find the force exerted by one magnet of the other.
Figure shows some of the equipotential surfaces of the magnetic scalar potential. Find the magnetic field B at a point in the region.
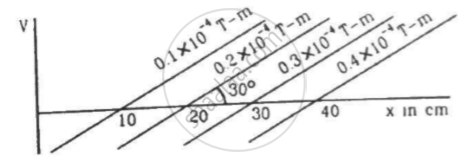
The magnetic field at a point, 10 cm away from a magnetic dipole, is found to be `2.0 xx 10^-4 "T"` . Find the magnetic moment of the dipole if the point is (a) in end-on position of the dipole and (b) in broadside-on position of the dipole.
A magnetic dipole of magnetic moment `1.44 "A m"^2`is placed horizontally with the north pole pointing towards north. Find the position of the neutral point if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 18 μT.
The coercive force for a certain permanent magnet is 4.0 × 104 A m−1. This magnet is placed inside a long solenoid of 40 turns/cm and a current is passed in the solenoid to demagnetise it completely. Find the current.
The magnetic moment of the assumed dipole at the earth's centre is 8.0 × 1022 A m2. Calculate the magnetic field B at the geomagnetic poles of the earth. Radius of the earth is 6400 km.
The magnetic field due to the earth has a horizontal component of 26 μT at a place where the dip is 60°. Find the vertical component and the magnitude of the field.
A magnetic needle is free to rotate in a vertical plane which makes an angle of 60° with the magnetic meridian. If the needle stays in a direction making an angle of `tan^-1(2sqrt(3))` with the horizontal, what would be the dip at that place?
A deflection magnetometer is placed with its arms in north-south direction. How and where should a short magnet having M/BH = 40 A m2 T−1 be placed so that the needle can stay in any position?
A bar magnet takes π/10 second the complete one oscillation in an oscillation magnetometer. The moment of inertia of the magnet about the axis of rotation is 1.2 × 10−4 kg m2 and the earth's horizontal magnetic field is 30 μT. Find the magnetic moment of the magnet.
Which property of soft iron makes it useful for preparing electromagnet?
In a permanent magnet at room temperature ______.
Assertion: Electromagnetic are made of soft iron.
Reason: Coercivity of soft iron is small.
The relation b/w magnetic susceptibility xm and relativ~ permeability µr is
