Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A magnetic needle is free to rotate in a vertical plane which makes an angle of 60° with the magnetic meridian. If the needle stays in a direction making an angle of `tan^-1(2sqrt(3))` with the horizontal, what would be the dip at that place?
उत्तर
Given :
Angle made by the magnetic meridian with the plane of rotation of the needle , `θ = 60^circ`
Angle made by the needle with the horizontal, `δ_1 = tan^-1(2/sqrt(3))`
If δ is the angle of dip , then
`tan δ_1 = tanδ/cosθ`
⇒ `tan δ = tan δ_1 cos θ`
⇒ `tan δ = tan (tan^-1 2/sqrt3) cos60^circ`
⇒ `tan δ = 2/sqrt(3) xx 1/2 = 1/sqrt(3)`
⇒ `δ = 30^circ`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State two advantages of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet.
Why is the core of an electromagnet made of ferromagnetic materials?
Compare the direction of the magnetic field inside a solenoid with that of the field there if the solenoid is replaced by its equivalent combination of north pole and south pole.
Magnetic scalar potential is defined as `U(vec r_2) - U(vec r_1) = - ∫_vec(r_1)^vec(r_2)` `vec (B) . dvec(l)`
Apply this equation to a closed curve enclosing a long straight wire. The RHS of the above equation is then `-u_0 i` by Ampere's law. We see that `U(vec(r_2)) ≠ U(vec(r_1))` even when `vec r_2 =vec r_1` .Can we have a magnetic scalar potential in this case?
A dip circle is taken to geomagnetic equator. The needle is allowed to move in a vertical plane perpendicular to the magnetic meridian. The needle will stay ______.
If the current is doubled, the deflection is also doubled in
To measure the magnetic moment of a bar magnet, one may use
(a) a tangent galvanometer
(b) a deflection galvanometer if the earth's horizontal field is known
(c) an oscillation magnetometer if the earth's horizontal field is known
(d) both deflection and oscillation magnetometer if the earth's horizontal field is not known
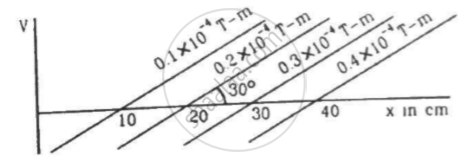
Figure shows some of the equipotential surfaces of the magnetic scalar potential. Find the magnetic field B at a point in the region.
Show that the magnetic field at a point due to a magnetic dipole is perpendicular to the magnetic axis if the line joining the point with the centre of the dipole makes an angle of `tan^-1(sqrt 2)` with the magnetic axis
If the earth's magnetic field has a magnitude 3.4 × 10−5 T at the magnetic equator of the earth, what would be its value at the earth's geomagnetic poles?
The needle of a dip circle shows an apparent dip of 45° in a particular position and 53° when the circle is rotated through 90°. Find the true dip.
A deflection magnetometer is placed with its arms in north-south direction. How and where should a short magnet having M/BH = 40 A m2 T−1 be placed so that the needle can stay in any position?
A bar magnet takes π/10 second the complete one oscillation in an oscillation magnetometer. The moment of inertia of the magnet about the axis of rotation is 1.2 × 10−4 kg m2 and the earth's horizontal magnetic field is 30 μT. Find the magnetic moment of the magnet.
A short magnet makes 40 oscillations per minute when used in an oscillation magnetometer at a place where the earth's horizontal magnetic field is 25 μT. Another short magnet of magnetic moment 1.6 A m2 is placed 20 cm east of the oscillating magnet. Find the new frequency of oscillation if the magnet has its north pole (a) towards north and (b) towards south.
What should be retentivity and coercivity of permanent magnet?
A thin diamagnetic rod is placed vertically between the poles of an electromagnet. When the current in the electromagnet is switched on, then the diamagnetic rod is pushed up, out of the horizontal magnetic field. Hence the rod gains gravitational potential energy. The work required to do this comes from ______.
The relation b/w magnetic susceptibility xm and relativ~ permeability µr is
Which of the following is most suitable for the core of an electromagnet?
