Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Compare the direction of the magnetic field inside a solenoid with that of the field there if the solenoid is replaced by its equivalent combination of north pole and south pole.
उत्तर
The direction of the magnetic field is the same in both cases, that is, inside a solenoid and inside a bar magnet. In a solenoid, magnetic field lines are directed from one end to the other internally and externally, so they are in the equivalent combination of north and south poles (as shown in figure).

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State any two advantages of electromagnets over permanent magnets.
What are permanent magnets? Give one example ?
Can we have a single north pole, or a single south pole?
Magnetic meridian is
A uniform magnetic field of `0.20 xx 10^-3 "T"` exists in the space. Find the change in the magnetic scalar potential as one moves through 50 cm along the field.
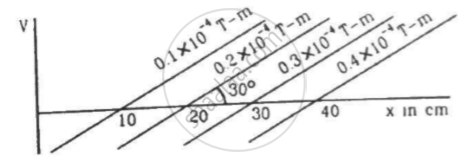
Figure shows some of the equipotential surfaces of the magnetic scalar potential. Find the magnetic field B at a point in the region.
A magnetic dipole of magnetic moment `1.44 "A m"^2`is placed horizontally with the north pole pointing towards north. Find the position of the neutral point if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 18 μT.
Do permeability and relative permeability have the same dimensions?
The desirable properties for making permanent magnets are _________________ .
If the earth's magnetic field has a magnitude 3.4 × 10−5 T at the magnetic equator of the earth, what would be its value at the earth's geomagnetic poles?
The magnetic field due to the earth has a horizontal component of 26 μT at a place where the dip is 60°. Find the vertical component and the magnitude of the field.
The needle of a dip circle shows an apparent dip of 45° in a particular position and 53° when the circle is rotated through 90°. Find the true dip.
A short magnet produces a deflection of 37° in a deflection magnetometer in Tan-A position when placed at a separation of 10 cm from the needle. Find the ratio of the magnetic moment of the magnet to the earth's horizontal magnetic field.
The magnetometer of the previous problem is used with the same magnet in Tan-B position. Where should the magnet be placed to produce a 37° deflection of the needle?
A bar magnet takes π/10 second the complete one oscillation in an oscillation magnetometer. The moment of inertia of the magnet about the axis of rotation is 1.2 × 10−4 kg m2 and the earth's horizontal magnetic field is 30 μT. Find the magnetic moment of the magnet.
A bar magnet makes 40 oscillations per minute in an oscillation magnetometer. An identical magnet is demagnetized completely and is placed over the magnet in the magnetometer. Find the time taken for 40 oscillations by this combination. Neglect any induced magnetism.
Choose the correct option:
Soft iron is used to make the core of the transformer because of its ______.
The relation b/w magnetic susceptibility xm and relativ~ permeability µr is
