Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The desirable properties for making permanent magnets are _________________ .
पर्याय
high retentivity and high coercive force
high retentivity and low coercive force
low retentivity and high coercive force
low retentivity and low coercive force
उत्तर
high retentivity and high coercive force
Permanent magnets should have high retentivity so that the magnet is strong and high coercive force, so that magnetisation is not erased by stary magnetic fields, temperature change or due to rough handling etc.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What are permanent magnets? Give one example ?
Why should the material used for making permanent magnets have high coercivity?
Compare the direction of the magnetic field inside a solenoid with that of the field there if the solenoid is replaced by its equivalent combination of north pole and south pole.
A dip circle is taken to geomagnetic equator. The needle is allowed to move in a vertical plane perpendicular to the magnetic meridian. The needle will stay ______.
Which of the following four graphs may best represent the current-deflection relation in a tangent galvanometer?
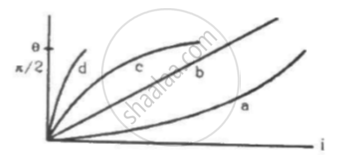
A tangent galvanometer is connected directly to an ideal battery. If the number of turns in the coil is doubled the deflection will
Two long bare magnets are placed with their axes coinciding in such a way that the north pole of the first magnet is 2.0 cm from the south pole of the second. If both the magnets have a pole strength of 10 Am, find the force exerted by one magnet of the other.
The magnetic field at a point, 10 cm away from a magnetic dipole, is found to be `2.0 xx 10^-4 "T"` . Find the magnetic moment of the dipole if the point is (a) in end-on position of the dipole and (b) in broadside-on position of the dipole.
Why is it not possible to make permanent magnets from paramagnetic materials?
The magnetic moment of the assumed dipole at the earth's centre is 8.0 × 1022 A m2. Calculate the magnetic field B at the geomagnetic poles of the earth. Radius of the earth is 6400 km.
The needle of a dip circle shows an apparent dip of 45° in a particular position and 53° when the circle is rotated through 90°. Find the true dip.
A moving-coil galvanometer has a 50-turn coil of size 2 cm × 2 cm. It is suspended between the magnetic poles producing a magnetic field of 0.5 T. Find the torque on the coil due to the magnetic field when a current of 20 mA passes through it.
A short magnet produces a deflection of 37° in a deflection magnetometer in Tan-A position when placed at a separation of 10 cm from the needle. Find the ratio of the magnetic moment of the magnet to the earth's horizontal magnetic field.
A bar magnet takes π/10 second the complete one oscillation in an oscillation magnetometer. The moment of inertia of the magnet about the axis of rotation is 1.2 × 10−4 kg m2 and the earth's horizontal magnetic field is 30 μT. Find the magnetic moment of the magnet.
A bar magnet makes 40 oscillations per minute in an oscillation magnetometer. An identical magnet is demagnetized completely and is placed over the magnet in the magnetometer. Find the time taken for 40 oscillations by this combination. Neglect any induced magnetism.
Choose the correct option:
Soft iron is used to make the core of the transformer because of its ______.
Answer in brief.
Explain one application of electromagnet.
A thin diamagnetic rod is placed vertically between the poles of an electromagnet. When the current in the electromagnet is switched on, then the diamagnetic rod is pushed up, out of the horizontal magnetic field. Hence the rod gains gravitational potential energy. The work required to do this comes from ______.
