Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What should be retentivity and coercivity of permanent magnet?
उत्तर
A permanent magnet should have a high zero-field magnetization and require a high reverse field to demagnetize. In other words, it should have a wide hysteresis loop with high retentivity and coercivity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State how magnetic susceptibility is different for the three types of magnetic materials, i.e. diamagnetic, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials
State two advantages of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet.
Why is the core of an electromagnet made of ferromagnetic materials?
Why should the material used for making permanent magnets have high coercivity?
Can we have a single north pole, or a single south pole?
The force on a north pole, `vecF = mvecB` , parallel to the field `vecB` . Does it contradict our earlier knowledge that a magnetic field can exert forces only perpendicular to itself?
A dip circle is taken to geomagnetic equator. The needle is allowed to move in a vertical plane perpendicular to the magnetic meridian. The needle will stay ______.
A very long bar magnet is placed with its north pole coinciding with the centre of a circular loop carrying as electric current i. The magnetic field due to the magnet at a point on the periphery of the wire is B. The radius of the loop is a. The force on the wire is
Consider the situation of the previous problem. The directions of the magnetic field due to the dipole are opposite at
(a) P1 and P2
(b) Q1 and Q2
(c) P1 and Q1
(d) P2 and Q2
Two long bare magnets are placed with their axes coinciding in such a way that the north pole of the first magnet is 2.0 cm from the south pole of the second. If both the magnets have a pole strength of 10 Am, find the force exerted by one magnet of the other.
A uniform magnetic field of `0.20 xx 10^-3 "T"` exists in the space. Find the change in the magnetic scalar potential as one moves through 50 cm along the field.
Figure shows some of the equipotential surfaces of the magnetic scalar potential. Find the magnetic field B at a point in the region.
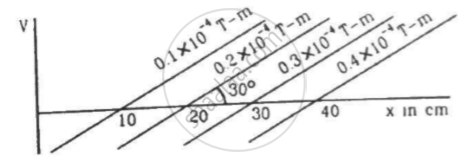
A magnetic dipole of magnetic moment `1.44 "A m"^2`is placed horizontally with the north pole pointing towards north. Find the position of the neutral point if the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is 18 μT.
A magnetic needle is free to rotate in a vertical plane which makes an angle of 60° with the magnetic meridian. If the needle stays in a direction making an angle of `tan^-1(2sqrt(3))` with the horizontal, what would be the dip at that place?
The needle of a dip circle shows an apparent dip of 45° in a particular position and 53° when the circle is rotated through 90°. Find the true dip.
A moving-coil galvanometer has a 50-turn coil of size 2 cm × 2 cm. It is suspended between the magnetic poles producing a magnetic field of 0.5 T. Find the torque on the coil due to the magnetic field when a current of 20 mA passes through it.
A short magnet produces a deflection of 37° in a deflection magnetometer in Tan-A position when placed at a separation of 10 cm from the needle. Find the ratio of the magnetic moment of the magnet to the earth's horizontal magnetic field.
A short magnet oscillates in an oscillation magnetometer with a time period of 0.10 s where the earth's horizontal magnetic field is 24 μT. A downward current of 18 A is established in a vertical wire placed 20 cm east of the magnet. Find the new time period.
A bar magnet makes 40 oscillations per minute in an oscillation magnetometer. An identical magnet is demagnetized completely and is placed over the magnet in the magnetometer. Find the time taken for 40 oscillations by this combination. Neglect any induced magnetism.
In a permanent magnet at room temperature ______.
Assertion: Electromagnetic are made of soft iron.
Reason: Coercivity of soft iron is small.
Which of the following is most suitable for the core of an electromagnet?
