Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Mark the correct statements:
पर्याय
The magnitude of the velocity of a particle is equal to its speed.
The magnitude of average velocity in an interval is equal to its average speed in that interval.
It is possible to have a situation in which the speed of a particle is always zero but the average speed is not zero.
It is possible to have a situation in which the speed of the particle is never zero but the average speed in an interval is zero.
उत्तर
The magnitude of the velocity of a particle is equal to its speed.
(a) Velocity being a vector quantity has magnitude as well as direction, and magnitude of velocity is called speed.
(b) Average velocity = \[\frac{\text{ Total displacement } }{\text{ Total time taken } }\]
Average speed = \[\frac{\text{ Total distance travelled } }{\text{ Total time taken } }\]
Distance \[\geq\] Displacement
∴ Average speed \[\geq\] Average velocity
The magnitude of average velocity in an interval is not always equal to its average speed in that interval.
(c) If speed is always zero, then the distance travelled is always zero. Hence, the total distance travelled and the average speed will be zero.
(d) If the speed of a particle is never zero, the distance travelled by the particle is never zero. Hence, the average speed will not be zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
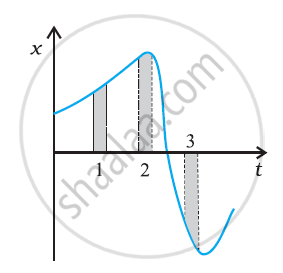
The following figure gives the x-t plot of a particle in one-dimensional motion. Three different equal intervals of time are shown. In which interval is the average speed greatest, and in which is it the least? Give the sign of average velocity for each interval.
A car travels at a speed of 60 km/hr due north and the other at a speed of 60 km/hr due east. Are the velocities equal? If no, which one is greater? If you find any of the questions irrelevant, explain.
A ball is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 20 m/s. Draw a graph showing the velocity of the ball as a function of time as it goes up and then comes back.
A motor car is going due north at a speed of 50 km/h. It makes a 90° left turn without changing the speed. The change in the velocity of the car is about ______.
A person travelling on a straight line moves with a uniform velocity v1 for some time and with uniform velocity v2 for the next equal time. The average velocity v is given by
The range of a projectile fired at an angle of 15° is 50 m. If it is fired with the same speed at an angle of 45°, its range will be
Pick the correct statements:
(a) Average speed of a particle in a given time is never less than the magnitude of the average velocity.
(b) It is possible to have a situation in which
(d) The average velocity of a particle moving on a straight line is zero in a time interval. It is possible that the instantaneous velocity is never zero in the interval. (Infinite accelerations are not allowed).
The velocity of a particle is zero at t = 0.
(a) The acceleration at t = 0 must be zero.
(b) The acceleration at t = 0 may be zero.
(c) If the acceleration is zero from t = 0 to t = 10 s, the speed is also zero in this interval.
(d) If the speed is zero from t = 0 to t = 10 s the acceleration is also zero in this interval.
In figure shows the position of a particle moving on the X-axis as a function of time.

It is 260 km from Patna to Ranchi by air and 320 km by road. An aeroplane takes 30 minutes to go from Patna to Ranchi whereas a delux bus takes 8 hours. Find the average speed of the plane.
It is 260 km from Patna to Ranchi by air and 320 km by road. An aeroplane takes 30 minutes to go from Patna to Ranchi whereas a delux bus takes 8 hours. Find the average velocity of the plane.
When a person leaves his home for sightseeing by his car, the meter reads 12352 km. When he returns home after two hours the reading is 12416 km. What is the average of velocity?
An athlete takes 2.0 s to reach his maximum speed of 18.0 km/h. What is the magnitude of this average acceleration.
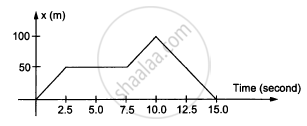
In the following figure shows the graph of the x-coordinate of a particle going along the X-axis as a function of time. Find the average velocity during 0 to 10 s,
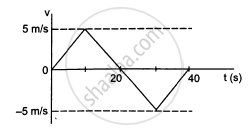
From the velocity-time plot shown in the following figure, find the distance travelled by the particle during the first 40 seconds. Also find the average velocity during this period.
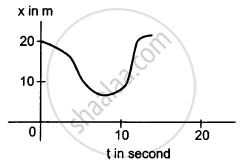
In the following figure shows x-t graph of a particle. Find the time t such that the average velocity of the particle during the period 0 to t is zero.
Among the four graphs (Figure), there is only one graph for which average velocity over the time intervel (0, T ) can vanish for a suitably chosen T. Which one is it?
