Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match the following:
|
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(a) |
cm3 |
(i) Pressure |
|
(b) |
Kelvin |
(ii) Temperature |
|
(c) |
Torr |
(iii) Volume |
|
(d) |
Boyle's law |
(iv) `"V"/"T" = ("V"_1)/("T"_1)` |
|
(a) |
Charles's law |
(v) `"PV"/"T" = ("P"_1 "V"_1)/"T"_1` |
|
|
|
(vi) PV = P1V1 |
उत्तर
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(a) cm3 |
Volume |
|
(b) Kelvin |
Temperature |
|
(c) Torr |
Pressure |
|
(d) Boyle's law |
PV = P1 V1
|
|
(e) Charles's law |
`"V"/"T" = ("V"_1)/("T"_1)` |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Estimate the total number of air molecules (inclusive of oxygen, nitrogen, water vapour and other constituents) in a room of capacity 25.0 m3 at a temperature of 27 °C and 1 atm pressure
Three vessels of equal capacity have gases at the same temperature and pressure. The first vessel contains neon (monatomic), the second contains chlorine (diatomic), and the third contains uranium hexafluoride (polyatomic).
Is the root mean square speed of molecules the same in the three cases? If not, in which case is vrms the largest?
What do you understand by gas?
Choose the correct answer:
The graph of PV vs P for gas is
Name or state the following:
The absolute temperature value corresponding to 35°C.
Give reason for the following:
Temperature remaining constant the product of the vol. & the press, of a given mass of dry gas is a constant.
Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at the temperature on the surface of the Sun (6000 K).
Three vessels of equal capacity have gases at the same temperature and pressure. The first vessel contains neon (monatomic), the second contains chlorine (diatomic), and the third contains uranium hexafluoride (polyatomic).
Do the vessels contain an equal number of respective molecules?
Which of the following diagrams (Figure) depicts ideal gas behaviour?
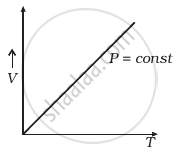 (a) |
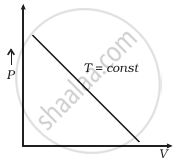 (b) |
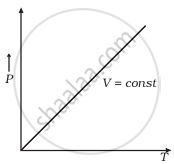 (c) |
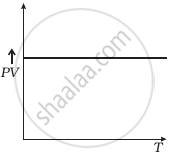 (d) |
Cooking gas containers are kept in a lorry moving with uniform speed. The temperature of the gas molecules inside will ______.
