Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
One of the following wavelengths is absent and the rest are present in the X-rays coming from a Coolidge tube. Which one is the absent wavelength?
पर्याय
25 pm
50 pm
75 pm
100 pm
उत्तर
25 pm
Cutoff wavelength (minimum) is absent in the X-rays coming from a Coolidge tube. Hence, the 25 pm wavelength is absent.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
To which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of frequency 5 × 1011 Hz belong?
Name the high energetic invisible electromagnetic waves which help in the study of the structure of crystals
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a) Gamma rays.
What is the range of the wavelength of the following electromagnetic waves?
(a)X-rays,
Name the waves used for taking photographs in dark.
X-ray from a Coolidge tube is incident on a thin aluminium foil. The intensity of the X-ray transmitted by the foil is found to be I0. The heating current is increased to increase the temperature of the filament. The intensity of the X-ray transmitted by the foil will be
(a) zero
(b) < I0
(c) I0
(d) > I0
The wavelength of Kα X-ray of tungsten is 21.3 pm. It takes 11.3 keV to knock out an electron from the L shell of a tungsten atom. What should be the minimum accelerating voltage across an X-ray tube having tungsten target which allows production of Kα X-ray?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
A free atom of iron emits Kα X-rays of energy 6.4 keV. Calculate the recoil kinetic energy of the atom. Mass of an iron atom = 9.3 × 10−26 kg.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
| Gamma rays | D | C | Visible light | B | A |
The above table shows different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
(a) Identify the parts of the spectrum marked as A, B, C and D.
(b) Which of the radiations A or B has the higher frequency?
(c) State two properties which are common to all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum.
(d) Name one source of each of the radiation of electromagnetic spectrum.
(e) Name one detector for each of the radiation.
(f) Name one use of each of the radiation.
Name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is:
Produced by bombarding a metal target with high electrons.
Choose the correct option.
The EM wave emitted by the Sun and responsible for heating the Earth’s atmosphere due to greenhouse effect is
Answer briefly.
Why light waves travel in a vacuum whereas sound waves cannot?
Answer briefly.
Give two uses of radio waves.
X-rays, gamma rays and microwaves travelling in a vacuum have ______.
The half-value thickness of an absorber is defined as the thickness that will reduce exponentially the intensity of a beam of particles by a factor of 2. The half-value thickness in (µm) for lead assuming X-ray beam of wavelength 20 pm, µ = 50 cm-1 for X-rays in lead at wavelength λ = 20 pm, is ______ µm.
Identify the electromagnetic wave whose wavelength range is from about 10-3 m to about 10-1 m. Write one use of this.
Identify the electromagnetic radiation and write its wavelength range, which is used to kill germs in water purified. Name the two sources of these radiations.
What happens when an electron collides with a positron?
In an atom X, electrons absorb the energy from an external source. This energy “excites” the electrons from a lower-energy level to a higher-energy level around the nucleus of the atom. When electrons return to the ground state, they emit photons.
The figure below is the energy level diagram of atom X with three energy levels, E1 = 0.00eV, E2 = 1.78eV and E3 = 2.95eV. The ground state is considered 0 eV for reference. The transition of electrons takes place between levels E1 and E2.
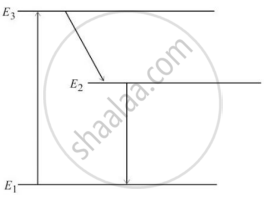
- What wavelength of radiation is needed to excite the atom to energy level E2 from E1?
- Suppose the external source has a power of 100 W. What would be the rate of photon emission?
