Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
S is the surface of a lump of magnetic material.
- Lines of B are necessarily continuous across S.
- Some lines of B must be discontinuous across S.
- Lines of H are necessarily continuous across S.
- Lines of H cannot all be continuous across S.
पर्याय
a and b
b and c
c and d
a and d
उत्तर
a and d
Explanation:
Here we are introducing the properties of magnetic field lines (B), for any magnet, it forms continuous closed loops. This is unlike the electric dipole where these field lines begin from a positive charge and end on the negative charge or escape to infinity.
Also, magnetic intensity (H) outside any magnet is H = `B/mu_0` and inside the magnet H = `B/(mu_0mu_r)`, where `mu_r` is the relative permeability of material (magnetic).
Magnetic field lines for magnetic field `(vecB)` is continuous upon a transition through the interface.
Also, magnetic intensity `(vecH)` varies for inside and outside the lump. So, lines of `(vecH)` cannot all be continuous across S.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A paramagnetic gas has 2.0 × 1026 atoms/m with atomic magnetic dipole moment of 1.5 × 10−23 A m2 each. The gas is at 27°C.
- Find the maximum magnetization intensity of this sample.
- If the gas in this problem is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 3 T, is it possible to achieve saturation magnetization? Why?
There are three needles 'N1', 'N2' and 'N3' made of a ferromagnetic, a paramagnetic and a diamagnetic substance respectively. When a magnet is brought close to them, then it will ____________.
The materials having negative magnetic susceptibility are ____________.
Is the permeability of a ferromagnetic material independent of the magnetic field? If not, is it more for lower or higher fields?
A Rowland ring of mean radius 15 cm has 3500 turns of wire wound on a ferromagnetic core of relative permeability 800. What is the magnetic field B in the core for a magnetising current of 1.2 A?
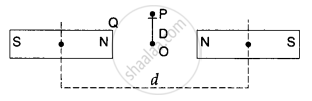
Two identical bar magnets are fixed with their centres at a distance d apart. A stationary charge Q is placed at P in between the gap of the two magnets at a distance D from the centre O as shown in the figure. The force on the charge Q is ______.
The universal property of all substances is ______.
A permanent magnet in the shape of a thin cylinder of length 10 cm has M = 106 A/m. Calculate the magnetisation current IM.
