Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A Rowland ring of mean radius 15 cm has 3500 turns of wire wound on a ferromagnetic core of relative permeability 800. What is the magnetic field B in the core for a magnetising current of 1.2 A?
उत्तर
Mean radius of a Rowland ring, r = 15 cm = 0.15 m
Number of turns on a ferromagnetic core, N = 3500
Relative permeability of the core material, μr = 800
Magnetising current, I = 1.2 A
The magnetic field is given by the relation:
B = `(μ_"r"μ_0"IN")/(2π"r")`
Where,
μ0 = Permeability of free space = 4π × 10−7 T mA−1
B = `(800 xx 4π xx 10^-7 xx 1.2 xx 3500)/(2π xx 0.15)`
= 4.48 T
Therefore, the magnetic field in the core is 4.48 T.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer in brief.
Discuss the Curie law for paramagnetic material.
A paramagnetic gas has 2.0 × 1026 atoms/m with atomic magnetic dipole moment of 1.5 × 10−23 A m2 each. The gas is at 27°C.
- Find the maximum magnetization intensity of this sample.
- If the gas in this problem is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 3 T, is it possible to achieve saturation magnetization? Why?
Magnetic field lines are always nearly normal to the surface of a ferromagnet at every point. (This fact is analogous to the static electric field lines being normal to the surface of a conductor at every point.) Why?
S is the surface of a lump of magnetic material.
- Lines of B are necessarily continuous across S.
- Some lines of B must be discontinuous across S.
- Lines of H are necessarily continuous across S.
- Lines of H cannot all be continuous across S.
A long solenoid has 1000 turns per metre and carries a current of 1 A. It has a soft iron core of µr = 1000. The core is heated beyond the Curie temperature, Tc.
- The H field in the solenoid is (nearly) unchanged but the B field decreases drastically.
- The H and B fields in the solenoid are nearly unchanged.
- The magnetisation in the core reverses direction.
- The magnetisation in the core diminishes by a factor of about 108.
A uniform magnetic field gets modified as shown in figure when two specimens A and B are placed in it.
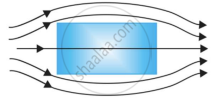 |
 |
| (a) | (b) |
- Identify the specimen A and B.
- How is the magnetic susceptibility of specimen A different from that of specimen B?
Magnetic susceptibility for a paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials is respectively ______.
- Assertion (A): Diamagnetic substances exhibit magnetism.
- Reason (R): Diamagnetic materials do not have a permanent magnetic dipole moment.
The relative magnetic permeability of a substance X is slightly less than unity and that of substance Y is slightly more than unity, then ______.
Explain ferromagnetism on the basis of the domain theory.
