Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Show that an ideal inductor does not dissipate power in an ac circuit.
उत्तर
Power = VIcos`phi`
For pure inductive circuit, the phase difference between current and voltage is `pi/2.`
∴ `phi = pi/2, cos phi = 0`
Therefore, zero power is dissipated. This current is sometimes referred to as watt-less current.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When an AC source is connected to an ideal inductor show that the average power supplied by the source over a complete cycle is zero.
An A.C. generator generating an emf of ε = 300 sin (100 πt) V is connected to a series combination of 16μ F capacitor, 1 H inductor and 100 Ω resistor.
Calculate :
1) An impedance of the circuit at the given frequency.
2) Resonant frequency `f_0`
3)Power factor at the resonant frequency `f_0`.
The power factor of an a.c. circuit is 0.5. What is the phase difference between voltage and current in this circuit ?
In a circuit, containing a capacitor and an AC source, the current is zero at the instant the source voltage is maximum. Is it consistent with Ohm's Law?
A resistance is connected to an AC source. If a capacitor is included in the series circuit, will the average power absorbed by the resistance increase or decrease? If an inductor of small inductance is also included in the series circuit, will the average power absorbed increase or decrease further?
An ac circuit as shown in the figure has an inductor of inductance L and a resistor of resistance R connected in series. Using the phasor diagram, explain why the voltage in the circuit will lead the current in phase.
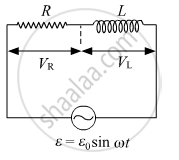
In previous questions 3 and 4, what is the net power absorbed by each circuit over a complete cycle. Explain your answer.
In which of the following circuits the maximum power dissipation is observed?
