Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An ac circuit as shown in the figure has an inductor of inductance L and a resistor of resistance R connected in series. Using the phasor diagram, explain why the voltage in the circuit will lead the current in phase.
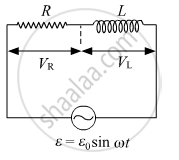
उत्तर
Phasor Diagram of the above circuit will be:
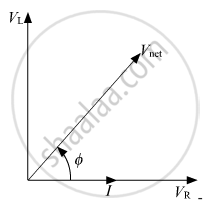
Net voltage `= sqrt("V"_2^2 + "V"_"R"^2)` will ahead of current by Φ
`tan phi = "V"_2/("V"_"R")`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
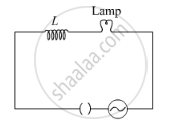
A lamp is connected in series with an inductor and an AC source. What happens to the brightness of the lamp when the key is plugged in and an iron rod is inserted inside the inductor? Explain.
An alternating emf of 220 V is applied to a circuit containing a resistor R having the resistance of 160Ω and a capacitor ‘C’ is series. The current is found to lead the supply voltage by an angle
`θ = tan^(-1) ("3/4")`
a) Calculate
1) The capacitive reactance
2) The impedance of the circuit
3) Current flowing in the circuit
b) If the frequency of the applied emf is 50 Hz, what is the value of the capacitance of the capacitor ‘C’?
In a circuit, containing a capacitor and an AC source, the current is zero at the instant the source voltage is maximum. Is it consistent with Ohm's Law?
Can you have an AC series circuit in which there is a phase difference of (a) 180° (b) 120° between the emf and the current?
An AC source rated 100 V (rms) supplies a current of 10 A (rms) to a circuit. The average power delivered by the source
(a) must be 1000 W
(b) may be 1000 W
(c) may be greater than 1000 W
(d) may be less than 1000 W
The current in a discharging LR circuit is given by i = i0 e−t/τ , where τ is the time constant of the circuit. Calculate the rms current for the period t = 0 to t = τ.
An electric bulb is designed to consume 55 W when operated at 110 volts. It is connected to a 220 V, 50 Hz line through a choke coil in series. What should be the inductance of the coil for which the bulb gets correct voltage?
In a series LCR circuit with an AC source, R = 300 Ω, C = 20 μF, L = 1.0 henry, εrms = 50 V and ν = 50/π Hz. Find (a) the rms current in the circuit and (b) the rms potential difference across the capacitor, the resistor and the inductor. Note that the sum of the rms potential differences across the three elements is greater than the rms voltage of the source.
A 100 Ω electric iron is connected to 200 V, 50 Hz ac source. Calculate average power delivered to iron, peak power and energy spent in one minute?
An alternating current I = 14 sin (100 πt) A passes through a series combination of a resistor of 30 Ω and an inductor of `(2/(5pi))` H. Taking `sqrt2` = 1.4 calculate the power factor of the circuit.
