Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2019-2020
Date: फेब्रुवारी 2020
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
- This question paper comprises four sections – A, B, C, and D.
- There are 37 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A: Q. no. 1 to 20 are very short-answer type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B: Q. no. 21 to 27 are short-answer type questions carrying 2 marks each.
- Section C: Q. no. 28 to 34 are long-answer type questions carrying 3 marks each.
- Section D: Q. no. 35 to 37 are also long answer type questions carrying 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in two questions of one mark, two questions of two marks, one question of three marks, and all the three questions of five marks. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
Choose the correct answer from given options
The wavelength and intensity of light emitted by a LED depend upon
forward bias and energy gap of the semiconductor
energy gap of the semiconductor and reverse bias
energy gap only
forward bias only
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Choose the correct answer from given options
The graph showing the correct variation of linear momentum (p) of a charge particle with its de-Broglie wavelength (λ) is _____________.

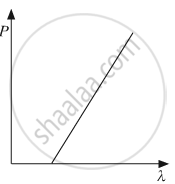
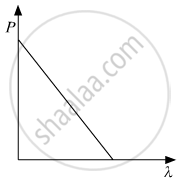
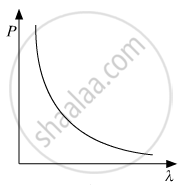
Chapter: [0.16] The Special Theory of Relativity
Choose the correct answer from given options
The selectivity of a series LCR a.c. circuit is large, when
L is large and R is large
L is small and R is small
L is large and R is small
L = R
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Choose the correct answer from given options
Photo diodes are used to detect
radio waves
gamma rays
IR rays
optical signals
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Choose the correct answer from given options
The relationship between Brewster angle θ and speed of light v in the denser medium is
c cosθ = v
v tanθ = c
c = v tanθ
v cosθ = c
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Choose the correct answer from given options
A biconvex lens of focal length f is cut into two identical plano-convex lenses. The focal length of each part will be
f
f/2
2f
4f
Chapter:
Choose the correct answer from given options
The phase difference between the current and the voltage in series LCR circuit at resonance is
π
π/2
π/3
zero
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Choose the correct answer from given options
Photons of frequency v are incident on the surface of two metals A and B of threshold frequency 3/4 v and 2/3 v, respectively. The ratio of maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted from A to that from B is
2 : 3
4 : 3
3: 4
3: 2
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Choose the correct answer from given options
The electric flux through a closed Gaussian surface depends upon
Net charge enclosed and permittivity of the medium
Net, charge enclosed, permittivity of the medium and the size of the Gaussian surface
Net charge enclosed only
Permittivity of the medium only
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Choose the correct answer from given options
A charge particle after being accelerated through a potential difference 'V' enters in a uniform magnetic field and moves in a circle of radius r. If V is doubled, the radius of the circle will become
2r
`sqrt(2r)`
4r
`r/sqrt(2)`
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Fill in the blank.
A point charge is placed at the centre of a hollow conducting sphere of internal radius 'r' and outer radius '2r'. The ratio of the surface charge density of the inner surface to that of the outer surface will be_________.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Fill in the blank.
The ___________, a property of materials C, Si, and Ge depends upon the energy gap between their conduction and valence bands.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Fill in the blank.
The ability of a junction diode to __________ an alternating voltage is based on the fact that it allows current to pass only when it is forward biased.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Fill in the blank.
The physical quantity having SI unit NC–1m is __________.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Fill in the blank.
A copper wire of the non-uniform area of cross-section is connected to a d.c. battery. The physical quantity, which remains constant along the wire is __________.
Chapter:
Answer the following question.
Write the conditions on path difference under which (i) constructive (ii) destructive interference occur in Young's double-slit experiment.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Plot a graph showing variation of induced e.m.f. with the rate of change of current flowing through a coil.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
A series combination of an inductor (L), capacitor (C) and a resistor (R) is connected across an ac source of emf of peak value E0, and angular frequency (ω). Plot a graph to show variation of impedance of the circuit with angular frequency (ω).
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Depict the fields diagram of an electromagnetic wave propagating along positive X-axis with its electric field along the Y-axis.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
An electron moves along +x direction. It enters into a region of uniform magnetic field. `vecB` directed along –z direction as shown in fig. Draw the shape of the trajectory followed by the electron after entering the field.
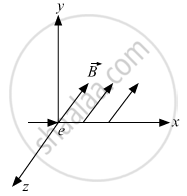
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Advertisements
A square shaped current carrying loop MNOP is placed near a straight long current carrying wire AB as shown in the fig. The wire and the loop lie in the same plane. If the loop experiences a net force F towards the wire, find the magnitude of the force on the side 'NO' of the loop.

Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Define the term 'current sensitivity' of a moving coil galvanometer.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A radioactive substance disintegrates into two types of daughter nuclei, one type with disintegration constant λ1 and the other type with disintegration constant λ2 . Determine the half-life of the radioactive substance.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Answer the following question.
In a single slit diffraction experiment, the width of the slit is increased. How will the (i) size and (ii) intensity of central bright band be affected? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
In the case of a photo electric effect experiment, explain the following facts, giving reasons.
The wave theory of light could not explain the existence of the threshold frequency.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
In the case of photoelectric effect experiment, explain the following facts, giving reasons.
The photoelectric current increases with increase of intensity of incident light.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Answer the following question.
Gamma rays and radio waves travel with the same velocity in free space. Distinguish between them in terms of their origin and the main application.
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Answer the following question.
Use Bohr's model of hydrogen atom to obtain the relationship between the angular momentum and the magnetic moment of the revolving electron.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Define the term 'wavefront of light'. A plane wavefront AB propagating from a denser medium (1) into a rarer medium (2) is incident of the surface P1P2 separating the two media as shown in fig.
Using Huygen's principle, draw the secondary wavelets and obtain the refracted wavefront in the diagram.
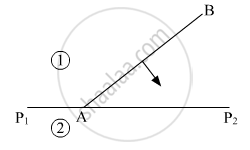
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Light from a sodium lamp (S) passes through two polaroid sheets P1 and P2 as shown in fig. What will be the effect on the intensity of the light transmitted (i) by P1 and (ii) by P2 on the rotating polaroid P1 about the direction of propagation of light? Justify your answer in both cases.

Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Answer the following question.
Obtain the expression for the energy stored in a capacitor connected across a dc battery. Hence define energy density of the capacitor
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Answer the following question.
Derive the expression for the torque acting on an electric dipole, when it is held in a uniform electric field. identify the orientation of the dipole in the electric field, in which it attains a stable equilibrium.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Answer the following question.
Two-point charges q1 and q2 are kept at a distance of r12 in air. Deduce the expression for the electrostatic potential energy of this system.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Answer the following question.
If an external electric field (E) is applied on the system, write the expression for the total energy of this system.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
What is a solar cell?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Answer the following question.
Draw solar cell V-I characteristics.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Answer the following question.
Explain the three processes involved in solar cell working.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Advertisements
Draw the circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier. Explain its working showing its input and output waveforms.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Define internal resistance of a cell.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Answer the following question.
A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected across a variable resistor R. Plot the shape of graphs showing a variation of terminal voltage V with (i) R and (ii) circuit current I.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Answer the following question.
Calculate the de-Broglie wavelength associated with the electron revolving in the first excited state of the hydrogen atom. The ground state energy of the hydrogen atom is – 13.6 eV.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Answer the following question.
When a conducting loop of resistance 10 Ω and area 10 cm2 is removed from an external magnetic field acting normally, the variation of induced current-I in the loop with time t is as shown in the figure.
Find the
(a) total charge passed through the loop.
(b) change in magnetic flux through the loop
(c) magnitude of the field applied
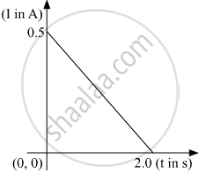
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Answer the following question.
Draw the curve showing the variation of binding energy per nucleon with the mass number of nuclei. Using it explains the fusion of nuclei lying on the ascending part and fission of nuclei lying on the descending part of this curve.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Answer the following question.
An optical instrument uses a lens of 100 D for the objective lens and 50 D for its eyepiece. When the tube length is kept at 20 cm, the final image is formed at infinity.
(a) Identify the optical instrument.
(b) Calculate the magnification produced by the instrument.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Answer the following question.
Write two important characteristics of equipotential surfaces.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Answer the following question.
A thin circular ring of radius r is charged uniformly so that its linear charge density becomes λ. Derive an expression for the electric field at a point P at a distance x from it along the axis of the ring. Hence, prove that at large distances (x >> r), the ring behaves as a point charge.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law on electrostatics and drive expression for the electric field due to a long straight thin uniformly charged wire (linear charge density λ) at a point lying at a distance r from the wire.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Answer the following question.
The magnitude of the electric field (in NC – 1) in a region varies with the distance r(in m) as
E = 10r + 5
By how much does the electric potential increase in moving from point at r = 11 m to a point at r = 10 m.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Define the term 'focal length of a mirror'.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Answer the following question.
With the help of a ray diagram, obtain the relation between its focal length and radius of curvature.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Answer the following question.
Calculate the angle of emergence (e) of the ray of light incident normally on the face AC of a glass prism ABC of refractive index `sqrt(3)`. How will the angle of emergence change qualitatively, if the ray of light emerges from the prism into a liquid of refractive index 1.3 instead of air?
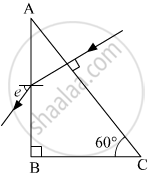
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Define the term 'resolving power of a telescope'. How will the resolving power be effected with the increase in
(i) Wavelength of light used.
(ii) Diameter of the objective lens.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A screen is placed 80 cm from an object. The image of the object on the screen is formed by a convex lens placed between them at two different locations separated by a distance 20 cm. determine the focal length of the lens.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Answer the following question.
Show that an ideal inductor does not dissipate power in an ac circuit.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
The variation of inductive reactance (XL) of an inductor with the frequency (f) of the ac source of 100 V and variable frequency is shown in fig.

(i) Calculate the self-inductance of the inductor.
(ii) When this inductor is used in series with a capacitor of unknown value and resistor of 10 Ω at 300 s–1, maximum power dissipation occurs in the circuit. Calculate the capacitance of the capacitor.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
A conductor of length 'l' is rotated about one of its ends at a constant angular speed 'ω' in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B. Plot graphs to show variations of the emf induced across the ends of the conductor with (i) angular speed ω and (ii) length of the conductor l.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Two concentric circular loops of radius 1 cm and 20 cm are placed coaxially.
(i) Find mutual inductance of the arrangement.
(ii) If the current passed through the outer loop is changed at a rate of 5 A/ms, find the emf induced in the inner loop. Assume the magnetic field on the inner loop to be uniform.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2019 - 2020
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2020 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
