Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law on electrostatics and drive expression for the electric field due to a long straight thin uniformly charged wire (linear charge density λ) at a point lying at a distance r from the wire.
उत्तर
Gauss' Law states that the net electric flux through any closed surface is equal to `1/epsilon_0` times the net electric charge within that closed surface.
`oint vec" E".d vec" s" = (q_(enclosed))/epsilon_o`
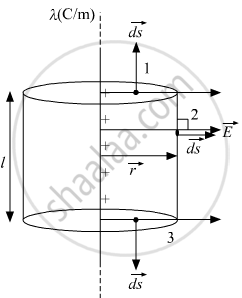
In the diagram, we have taken a cylindrical gaussian surface of radius = r and length = l.
The net charge enclosed inside the gaussian surface `q_(enclosed) = lambdal`
By symmetry, we can say that the Electric field will be in radially outward direction.
According to gauss' law,
`oint vec"E".d vec"s" = q_(enclosed)/epsilon_o`
`int_1 vec"E" .d vec"s" + int_2 vec"E" .d vec"s" + int_3 vec"E". d vec"s" = (lambdal)/epsilon_o`
`int_1 vec"E". d vec"s" & int_3 vec"E". d vec"s" "are zero", "Since" vec"E" "is perpendicular to" d vec"s"`
`int_2 vec"E" . d vec"s" = (lambdal)/epsilon_o`
`"at" 2, vec"E" and d vec"s" "are in the same direction, we can write"`
`E.2pirl = (lambdal)/epsilon_o`
`E = lambda/(2piepsilon_o r)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
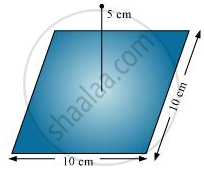
A point charge +10 μC is a distance 5 cm directly above the centre of a square of side 10 cm, as shown in the Figure. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the square? (Hint: Think of the square as one face of a cube with edge 10 cm.)
A thin conducting spherical shell of radius R has charge Q spread uniformly over its surface. Using Gauss’s law, derive an expression for an electric field at a point outside the shell.
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law for magnetism. Explain its significance.
The Electric flux through the surface
 (i) |
 (ii) |
 (iii) |
 (iv) |
Consider a region inside which there are various types of charges but the total charge is zero. At points outside the region
- the electric field is necessarily zero.
- the electric field is due to the dipole moment of the charge distribution only.
- the dominant electric field is `∞ 1/r^3`, for large r, where r is the distance from a origin in this region.
- the work done to move a charged particle along a closed path, away from the region, will be zero.
Refer to the arrangement of charges in figure and a Gaussian surface of radius R with Q at the centre. Then
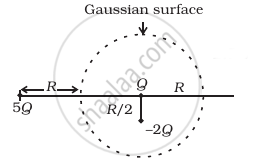
- total flux through the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/ε_0`.
- field on the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/(4 piε_0 R^2)`.
- flux through the surface of sphere due to 5Q is zero.
- field on the surface of sphere due to –2Q is same everywhere.
An arbitrary surface encloses a dipole. What is the electric flux through this surface?
If the total charge enclosed by a surface is zero, does it imply that the elecric field everywhere on the surface is zero? Conversely, if the electric field everywhere on a surface is zero, does it imply that net charge inside is zero.
A charge Q is placed at the centre of a cube. The electric flux through one of its faces is ______.
