Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider a region inside which there are various types of charges but the total charge is zero. At points outside the region
- the electric field is necessarily zero.
- the electric field is due to the dipole moment of the charge distribution only.
- the dominant electric field is `∞ 1/r^3`, for large r, where r is the distance from a origin in this region.
- the work done to move a charged particle along a closed path, away from the region, will be zero.
पर्याय
b and d
a and c
b and d
c and d
उत्तर
c and d
Explanation:
From Gauss’ law, we know `oint_s` E.dS = `q_(enclosed)/ε_0` in left side equation.
The electric field is due to all the charges present both inside as well as outside the Gaussian surface. Hence if `q_(enclosed)` = 0, it cannot be said that the electric field is necessarily zero.
If there are various types of charges in a region and total charge is zero, the region may be supposed to contain a number of electric dipoles.
Therefore, at points outside the region (maybe anywhere w.r.t. electric dipoles), the dominant electric field `∞ 1/r^3` for large r.
The electric field is conservative, work done to move a charged particle along a closed path, away from the region will be zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State and explain Gauss’s law.
A thin conducting spherical shell of radius R has charge Q spread uniformly over its surface. Using Gauss’s law, derive an expression for an electric field at a point outside the shell.
Draw a graph of electric field E(r) with distance r from the centre of the shell for 0 ≤ r ≤ ∞.
Which of the following statements is not true about Gauss’s law?
Gauss' law helps in ______
The Electric flux through the surface
 (i) |
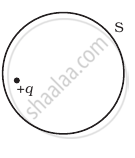 (ii) |
 (iii) |
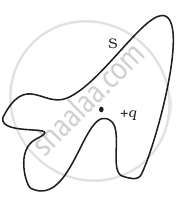 (iv) |
Five charges q1, q2, q3, q4, and q5 are fixed at their positions as shown in figure. S is a Gaussian surface. The Gauss’s law is given by `oint_s E.ds = q/ε_0`
Which of the following statements is correct?
An arbitrary surface encloses a dipole. What is the electric flux through this surface?
A charge Q is placed at the centre of a cube. The electric flux through one of its faces is ______.
