Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Five charges q1, q2, q3, q4, and q5 are fixed at their positions as shown in figure. S is a Gaussian surface. The Gauss’s law is given by `oint_s E.ds = q/ε_0`
Which of the following statements is correct?
पर्याय
E on the LHS of the above equation will have a contribution from q1, q5 and q3 while q on the RHS will have a contribution from q2 and q4 only.
E on the LHS of the above equation will have a contribution from all charges while q on the RHS will have a contribution from q2 and q4 only.
E on the LHS of the above equation will have a contribution from all charges while q on the RHS will have a contribution from q1, q3 and q5 only.
Both E on the LHS and q on the RHS will have contributions from q2 and q4 only.
उत्तर
E on the LHS of the above equation will have a contribution from all charges while q on the RHS will have a contribution from q2 and q4 only.
Explanation:
According to Gauss’ law, the term `q_(enclosed)` on the right side of the equation `oint_s E.ds = q_(enclosed)/ε_0` includes the sum of all charges enclosed by the surface called (Gaussian surface). In left side equation, the electric field is due to all the charges present both inside as well as outside the Gaussian surface.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A charge Q is placed at the centre of a cube. Find the flux of the electric field through the six surfaces of the cube.
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law on electrostatics and drive expression for the electric field due to a long straight thin uniformly charged wire (linear charge density λ) at a point lying at a distance r from the wire.
Gaussian surface cannot pass through discrete charge because ____________.
The Gaussian surface ______.
The surface considered for Gauss’s law is called ______.
Which of the following statements is not true about Gauss’s law?
Gauss' law helps in ______
If `oint_s` E.dS = 0 over a surface, then ______.
- the electric field inside the surface and on it is zero.
- the electric field inside the surface is necessarily uniform.
- the number of flux lines entering the surface must be equal to the number of flux lines leaving it.
- all charges must necessarily be outside the surface.
Refer to the arrangement of charges in figure and a Gaussian surface of radius R with Q at the centre. Then
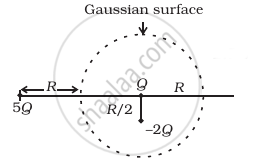
- total flux through the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/ε_0`.
- field on the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/(4 piε_0 R^2)`.
- flux through the surface of sphere due to 5Q is zero.
- field on the surface of sphere due to –2Q is same everywhere.
The region between two concentric spheres of radii a < b contain volume charge density ρ(r) = `"c"/"r"`, where c is constant and r is radial- distanct from centre no figure needed. A point charge q is placed at the origin, r = 0. Value of c is in such a way for which the electric field in the region between the spheres is constant (i.e. independent of r). Find the value of c:
