Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
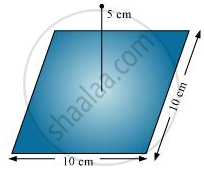
A point charge +10 μC is a distance 5 cm directly above the centre of a square of side 10 cm, as shown in the Figure. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the square? (Hint: Think of the square as one face of a cube with edge 10 cm.)
उत्तर
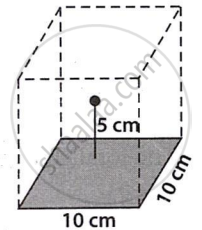
Based on the illustration, we can assume that the given square represents one side of a cube with an edge length of 10 cm.
The cube encloses the +10 µC charge because it is located 5 cm above the square's center. According to Gauss's theorem, cube-linked electric flow is
Φ = `q/ε_0`
= `(10 xx 10^-6)/(8.85 xx 10^-12)`
= 1.13 × 106 N m2 C−1
Consequently, the electromotive force acting on the square
Φsq = `"Φ"/6`
= `1.13/6 xx 10^6`
or Φsq = 1.9 × 105 N m2 C−1
संबंधित प्रश्न
A charge ‘q’ is placed at the centre of a cube of side l. What is the electric flux passing through each face of the cube?
State Gauss’s law for magnetism. Explain its significance.
Answer the following question.
State Gauss's law on electrostatics and drive expression for the electric field due to a long straight thin uniformly charged wire (linear charge density λ) at a point lying at a distance r from the wire.
Gaussian surface cannot pass through discrete charge because ____________.
q1, q2, q3 and q4 are point charges located at points as shown in the figure and S is a spherical gaussian surface of radius R. Which of the following is true according to the Gauss' law?

The Gaussian surface ______.
The surface considered for Gauss’s law is called ______.
Which of the following statements is not true about Gauss’s law?
The Electric flux through the surface
 (i) |
 (ii) |
 (iii) |
 (iv) |
If there were only one type of charge in the universe, then ______.
- `oint_s` E.dS ≠ 0 on any surface.
- `oint_s` E.dS = 0 if the charge is outside the surface.
- `oint_s` E.dS could not be defined.
- `oint_s` E.dS = `q/ε_0` if charges of magnitude q were inside the surface.
Consider a region inside which there are various types of charges but the total charge is zero. At points outside the region
- the electric field is necessarily zero.
- the electric field is due to the dipole moment of the charge distribution only.
- the dominant electric field is `∞ 1/r^3`, for large r, where r is the distance from a origin in this region.
- the work done to move a charged particle along a closed path, away from the region, will be zero.
Refer to the arrangement of charges in figure and a Gaussian surface of radius R with Q at the centre. Then
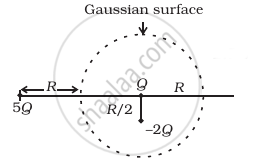
- total flux through the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/ε_0`.
- field on the surface of the sphere is `(-Q)/(4 piε_0 R^2)`.
- flux through the surface of sphere due to 5Q is zero.
- field on the surface of sphere due to –2Q is same everywhere.
If the total charge enclosed by a surface is zero, does it imply that the elecric field everywhere on the surface is zero? Conversely, if the electric field everywhere on a surface is zero, does it imply that net charge inside is zero.
In 1959 Lyttleton and Bondi suggested that the expansion of the Universe could be explained if matter carried a net charge. Suppose that the Universe is made up of hydrogen atoms with a number density N, which is maintained a constant. Let the charge on the proton be: ep = – (1 + y)e where e is the electronic charge.
- Find the critical value of y such that expansion may start.
- Show that the velocity of expansion is proportional to the distance from the centre.
In finding the electric field using Gauss law the formula `|vec"E"| = "q"_"enc"/(epsilon_0|"A"|)` is applicable. In the formula ε0 is permittivity of free space, A is the area of Gaussian surface and qenc is charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface. This equation can be used in which of the following situation?
A charge Q is placed at the centre of a cube. The electric flux through one of its faces is ______.
