Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
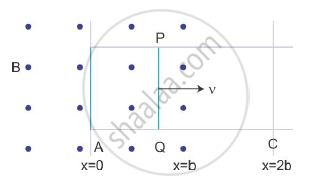
Sketch the change in flux, emf and force when a conducting rod PQ of resistance R and length l moves freely to and fro between A and C with speed v on a rectangular conductor placed in uniform magnetic field as shown in the figure
उत्तर
The flux enclosed by the rod is
Φ = Blx for 0 ≤ x ≤ b
= Blx for b ≤ x ≤ 2b
Now, the magnitude of induced emf is
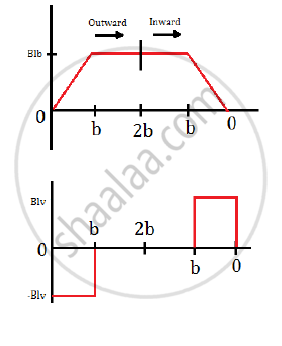
`epsilon=(dphi)/dt=-Bl(dx)/dt= -Blv` for 0 ≤ x ≤ b
`=-Bl(db)/dt=0` for b ≤ x ≤ 2b
Now, the magnitude of induced current when induced emf is non-zero is ε = IR
`:.I=epsilon/r=(Blv)/r`
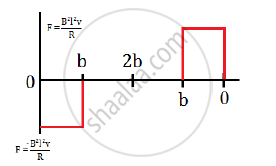
The force required to keep the conductor in motion is F = BIl
`:.F=B(Blv)/Rl=(B^2l^2v)/R`
`:.F=(B^2l^2v)/R` for b ≤ x < b
= 0 for b ≤ x ≤ 2b
Therefore, the variation of flux, emf and force is
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A small compass needle of magnetic moment ‘m’ is free to turn about an axis perpendicular to the direction of uniform magnetic field ‘B’. The moment of inertia of the needle about the axis is ‘I’. The needle is slightly disturbed from its stable position and then released. Prove that it executes simple harmonic motion. Hence deduce the expression for its time period.
You are facing a circular wire carrying an electric current. The current is clockwise as seen by you. Is the field at the centre coming towards you or going away from you?
A vertical wire carries a current in upward direction. An electron beam sent horizontally towards the wire will be deflected
Two parallel wires carry currents of 20 A and 40 A in opposite directions. Another wire carying a current anti parallel to 20 A is placed midway between the two wires. T he magnetic force on it will be
Consider a solid sphere of radius r and mass m that has a charge q distributed uniformly over its volume. The sphere is rotated about its diameter with an angular speed ω. Show that the magnetic moment µ and the angular momentum l of the sphere are related as `mu = q/(2m) l`
Consider a straight piece of length x of a wire carrying a current i. Let P be a point on the perpendicular bisector of the piece, situated at a distance d from its middle point. Show that for d >> x, the magnetic field at P varies as 1/d2 whereas for d << x, it varies as 1/d.
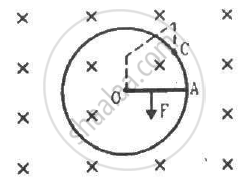
Consider the situation shown in the figure. Suppose the circular loop lies in a vertical plane. The rod has a mass m. The rod and the loop have negligible resistances but the wire connecting O and C has a resistance R. The rod is made to rotate with a uniform angular velocity ω in the clockwise direction by applying a force at the midpoint of OA in a direction perpendicular to it. Find the magnitude of this force when the rod makes an angle θ with the vertical.
A straight horizontal conducting rod of length 0.45 m and mass 60 g is suspended by two vertical wires at its ends. A current of 5.0 A is set up in the rod through the wires.
(a) What magnetic field should be set up normal to the conductor in order that the tension in the wires is zero?
(b) What will be the total tension in the wires if the direction of current is reversed keeping the magnetic field same as before?
(Ignore the mass of the wires) g = 9.8 m s–2.
When a magnetic compass needle is carried nearby to a straight wire carrying current, then
- the straight wire cause a noticeable deflection in the compass needle.
- the alignment of the needle is tangential to an imaginary circle with straight wire as its centre and has a plane perpendicular to the wire.
A straight conductor of length 2m moves at a speed of 20 m/s. When the conductor makes an angle of 30° with the direction of magnetic field of induction of 0.1 wbm2 then induced emf:
