Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State and explain Kepler's laws of planetary motion. Draw diagrams to illustrate these laws.
उत्तर
- Kepler's first law: The planets move in elliptical orbits around the sun, with the sun at one of the two foci. of the elliptical orbit. This law means that the orbit of a planet around the sun is an ellipse and not an exact circle. An elliptical path has two foci, and the sun is at one of the two foci of the elliptical path.

- Kepler's Second law: Each planet revolves around the sun in such a way that the line joining the planet to the sun sweeps over equal areas in equal intervals of time. This means that a planet does not move with constant speed around the sun. The speed is greater when the planet is nearer the sun and less when the planet is farther away from the sun.

- Kepler's Third Law: The cube of the mean distance of a planet from the sun is directly proportional to the square of time it takes to move around the sun. r3 ∝ T2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and a 1 kg object on its surface? (Mass of the earth is 6 × 1024 kg and radius of the earth is 6.4 × 106 m).
Choose the correct alternative:
Acceleration due to gravity increases/decreases with increasing altitude.
How will you ‘weigh the sun’, that is estimate its mass? The mean orbital radius of the earth around the sun is 1.5 × 108 km.
State Kepler’s law which is represented by the relation r3 ∝ T2.
State the universal law of gravitation. Name the scientist who gave this law.
A tunnel is dug along a chord of the earth at a perpendicular distance R/2 from the earth's centre. The wall of the tunnel may be assumed to be frictionless. Find the force exerted by the wall on a particle of mass m when it is at a distance x from the centre of the tunnel.
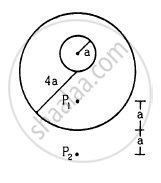
A uniform metal sphere of radius a and mass M is surrounded by a thin uniform spherical shell of equal mass and radius 4a (In the following figure). The centre of the shell falls on the surface of the inner sphere. Find the gravitational field at the points P1 and P2 shown in the figure.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The mass of earth is 6 × 1024 kg and radius of earth is 6.4 × 106 m. The magnitude of force between the mass of 1 kg and the earth is:
Solve the following problem.
Calculate the acceleration due to gravity at a height of 300 km from the surface of the Earth. (M = 5.98 × 1024 kg, R = 6400 km).
Three uniform spheres, each having mass m and radius r, are kept in such a way that each touches the other two. The magnitude of the gravitational force on any sphere due to the other two is
