Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State if the following statement is true or false. Give a reason for your answer.
In an elastic collision of two bodies, the momentum and energy of each body is conserved.
पर्याय
True
False
उत्तर
This statement is False.
Explanation:
In an elastic collision, the total energy and momentum of the two bodies combined, rather than of each body individually, are conserved.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State if the following statement is true or false. Give a reason for your answer.
In an inelastic collision, the final kinetic energy is always less than the initial kinetic energy of the system.
Answer the following question.
Obtain its value for an elastic collision and a perfectly inelastic collision.
Answer the following question.
Discuss the following as special cases of elastic collisions and obtain their exact or approximate final velocities in terms of their initial velocities.
- Colliding bodies are identical.
- A very heavy object collides on a lighter object, initially at rest.
- A very light object collides on a comparatively much massive object, initially at rest.
A bomb of mass 9 kg explodes into two pieces of mass 3 kg and 6 kg. The velocity of mass 3 kg is 16 m/s, The kinetic energy of mass 6 kg is ____________.
A block of mass 'm' moving along a straight line with constant velocity `3vec"v"` collides with another block of same mass at rest. They stick together and move with common velocity. The common velocity is ______.
A ball of mass m, moving with a speed 2v0, collides inelastically (e > 0) with an identical ball at rest. Show that for a general collision, the angle between the two velocities of scattered balls is less than 90°.
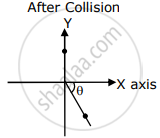
A ball of mass 10 kg moving with a velocity of 10`sqrt3` ms–1 along the X-axis, hits another ball of mass 20 kg which is at rest. After collision, the first ball comes to rest and the second one disintegrates into two equal pieces. One of the pieces starts moving along Y-axis at a speed of 10 m/s. The second piece starts moving at a speed of 20 m/s at an angle θ (degree) with respect to the X-axis.
The configuration of pieces after the collision is shown in the figure.
The value of θ to the nearest integer is ______.
A ball falls from a height of 1 m on a ground and it loses half its kinetic energy when it hits the ground. What would be the total distance covered by the ball after sufficiently long time?
A ball is thrown upwards from the foot of a tower. The ball crosses the top of tower twice after an interval of 4 seconds and the ball reaches ground after 8 seconds, then the height of tower is ______ m. (g = 10 m/s2)
A sphere of mass 'm' moving with velocity 'v' collides head-on another sphere of same mass which is at rest. The ratio of final velocity of second sphere to the initial velocity of the first sphere is ______. ( e is coefficient of restitution and collision is inelastic)
