Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the types (or kinds) of lever, and give two examples of each kind.
उत्तर
There are three kinds of the lever, depending upon the different positions of the load, fulcrum and the effort.
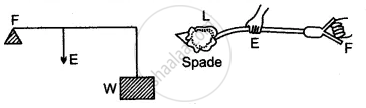
Type I: When fulcrum is in the middle.

Type II: When the load is between the fulcrum and the effort.
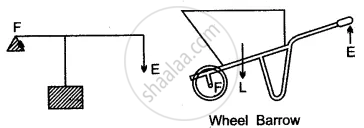
Type III: When the effort lies between the fulcrum and load.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is a lever?
Class II levers are designed to have ______.
A lever of length 9 cm has its load arm 5 cm long and the effort arm is 9 cm long.
- To which class does it belong?
- Draw a diagram of the lever showing the position of fulcrum F and directions of both the load L and effort E.
- What is the mechanical advantage and velocity ratio if the efficiency is 100%?
- What will be the mechanical advantage and velocity ratio if the efficiency becomes 50%?
Which type of levers have mechanical advantage always more than 1? Give reasons.
The following belong to which class of lever?
The Physical balance
The following belong to which class of lever?
Human-arm
The following belong to which class of lever?
A fire tongs
In the following diagram of a wheelbarrow, mark the fulcrum (F) and indicate the directions of load (L) and effort (E) with arrows.
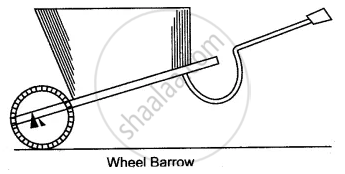
What class of lever is it? Give one more example of the same class of lever.
The diagram shows the use of a lever.
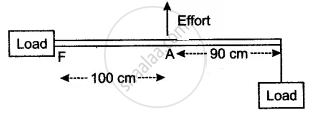
- State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever.
- Which class of lever is this? Give an example of this class of lever.
- If FA = 100 cm, AB = 90 cm, calculate the minimum effort required to lift the load.
The length of a nut-cracker is 12 cm. A nut, when kept at a distance of 4 cm from its fulcrum, requires an effort of 100 gf to crack it. What force will be required to crack the nut without using the nut-cracker?
