Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the underlying principle of a cyclotron. Write briefly how this machine is used to accelerate charged particles to high energies
Draw a schematic sketch of a cyclotron. Explain, giving the essential details of its construction, how it is used to accelerate the charged particles.
उत्तर १
It consists of two D-shaped hollow semicircular metal chambers D1 and D2, which are called dees. The two dees are placed horizontally with a small gap separating them. The dees are connected to the source of high frequency electric field. The dees are enclosed in a metal box containing a gas at a low pressure of the order of 10-3 mm mercury. The whole apparatus is placed between two poles of an electromagnet. The magnetic field acts perpendicular to the dees. The positive ions are produced in the gap between the two dees by ionisation of the gas.
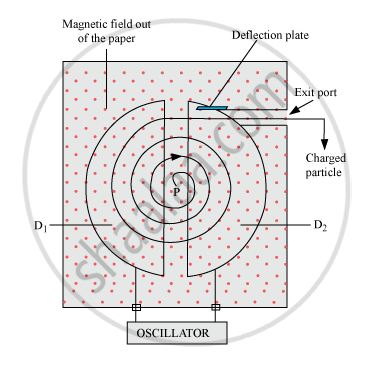
A cyclotron involves the use of an electric field to accelerate charged particles across the gap between the two D-shaped magnetic field regions. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the paths of the charged particles that makes them follow in circular paths within the two dees. An alternating voltage accelerates the charged particles each time they cross the dees. The radius of each particle’s path increases with its speed. So, the accelerated particles spiral toward the outer wall of the cyclotron
Square wave electric fields are used to accelerate the charged particles in a cyclotron.
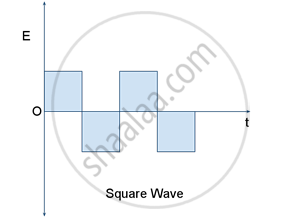
The accelerating electric field reverses just at the time the charged particle finishes its half circle, so that it gets accelerated across the gap between the dees.
The particle gets accelerated again and again, and its velocity increases. Therefore, it attains high kinetic energy
उत्तर २
The underlying principle of a cyclotron is that an oscillating electric field can be used to accelerate a charge particle to high energy.
A cyclotron involves the use of an electric field to accelerate charge particles across the gap between the two D-shaped magnetic field regions. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the paths of the charged particles that makes them follow in circular paths within the two Ds. An alternating voltage accelerates the charged particles each time they cross the Ds. The radius of each particle’s path increases with its speed. So, the accelerated particles spiral toward the outer wall of the cyclotron

[The Ds are the semi-circular structures (D1 and D2) between which the charges move. The accelerating voltage is maintained across the opposite halves of the Ds.]
Square wave electric fields are used to accelerate the charged particles in a cyclotron
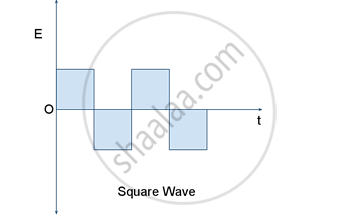
The accelerating electric field reverses just at the time the charge particle finishes its half circle so that it gets accelerated across the gap between the Ds.
The particle gets accelerated again and again, and its velocity increases. Therefore, it attains high kinetic energy
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a cyclotron, magnetic field of 3·5Wb/m2 is used to accelerate protons. What should be the time interval in which the electric field between the Dees be reversed?
(Mass of proton = 1· 67 x 10-27Kg, Charge on proton =1·6x10-19c).
Show that the time period of revolution of particles in a cyclotron is independent of their speeds. Why is this property necessary for the operation of a cyclotron?
A proton and an electron travelling along parallel paths enter a region of uniform magnetic field, acting perpendicular to their paths. Which of them will move in a circular path with higher frequency?
An α-particle and a proton are released from the centre of the cyclotron and made to accelerate.
(i) Can both be accelerated at the same cyclotron frequency?
Give reason to justify your answer.
(ii) When they are accelerated in turn, which of the two will have higher velocity at the exit slit of the does?
A cyclotron is used to accelerate protons to a kinetic energy of 5 MeV. If the strength of magnetic field in the cyclotron is 2T, find the radius and the frequency needed for the applied alternating voltage of the cyclotron. (Given : Velocity of proton= `3xx10^7 m//s`)
Two metal strips, each of length l, are clamped parallel to each other on a horizontal floor with a separation b between them. A wire of mass m lies on them perpendicularly, as shown in the figure. A vertically-upward magnetic field of strength B exists in the space. The metal strips are smooth but the coefficient of friction between the wire and the floor is µ. A current i is established when the switch S is closed at the instant t = 0. Discuss the motion of the wire after the switch is closed. How far away from the strips will the wire reach?
A cyclotron's oscillator frequency is 10 MHz. What should be the operating magnetic field for accelerating protons? If the radius of its 'dees' is 60 cm, calculate the kinetic energy (in MeV) of the proton beam produced by the accelerator.
A charged particle is moving in a cyclotron, what effect on the radius of path of this charged particle will occur when the frequency of the ratio frequency field is doubled?
Describe the motion of a charged particle in a cyclotron if the frequency of the radio frequency (rf) field were doubled.
