Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the underlying principle of working of a moving coil galvanometer. Write two reasons why a galvanometer can not be used as such to measure current in a given circuit. Name any two factors on which the current sensitivity of a galvanometer depends.
उत्तर
The underlying principle for the working of a moving coil galvanometer is that when a current-carrying conductor is placed inside a magnetic field, it experiences a magnetic force.
The two reasons why a galvanometer cannot be used for measuring current are
-
The high resistance of galvanometer can disturb the original current flowing through the circuit
-
The high current present in the circuit can destroy the coil windings present in the galvanometer
The factors on which the current sensitivity of a galvanometer depends are
-
Number of turns in the coil
-
Torsional spring constant
-
Area of the coil
-
Strength of the magnetic field
(Any two can be taken as the answer)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why does a galvanometer show a momentary deflection at the time of charging or discharging a capacitor? Write the necessary expression to explain this observation.
Draw a labelled diagram of a moving coil galvanometer. Describe briefly its principle and working.
Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity. Explain, giving reason.
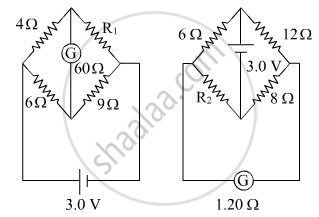
Figure shows two circuits each having a galvanometer and a battery of 3V.
When the galvanometers in each arrangement do not show any deflection, obtain the ratio R1/R2.
A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 12 Ω and the metre shows full scale deflection for a current of 3 mA. How will you convert the metre into a voltmeter of range 0 to 18 V?
A galvanometer coil has a resistance of 15 Ω and the metre shows full scale deflection for a current of 4 mA. How will you convert the metre into an ammeter of range 0 to 6 A?
Assertion (A): On Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer by increasing the number of turns may not necessarily increase its voltage sensitivity.
Reason (R): The resistance of the coil of the galvanometer increases on increasing the number of turns.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
A galvanometer coil bas 500 turns and each tum has an average area of 3 × 10-4 m2. If a torque of 1.5 Nm is required to keep this coil parallel to a magnetic field when a current of 0.5 A is flowing through it, the strength of the field (in T) is ______.
A resistance of 3Ω is connected in parallel to a galvanometer of resistance 297Ω. Find the fraction of current passing through the galvanometer.
