Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suggest a way to determine the `∧_"m"^∘`value of water.
उत्तर
Water is a weak electrolyte. Its `∧_"m"^∘`value can be determined with the help of Kohlrausch's law.
`∧_"m"^∘("HCl") = ∧_"m"^∘("H"^+) + ∧_"m"^∘("Cl"^-)` ...(i)
`∧_"m"^∘("NaOH") = ∧_"m"^∘("Na"^+) + ∧_"m"^∘("OH"^-)` ...(ii)
`∧_"m"^∘("NaCl") = ∧_"m"^∘("Na"^+) + ∧_"m"^∘("Cl"^-)` ...(iii)
By adding (i) and (ii) and subtracting (iii) we get
`∧_"m"^∘("H"_2"O") = ∧_"m"^∘("H"^+) + ∧_"m"^∘("OH"^-)`
= `∧_"m"^∘("HCl") + ∧_"m"^∘("NaOH") - ∧_"m"^∘("NaCl")`
संबंधित प्रश्न
The molar conductivity of cation and anion of salt BA are 180 and 220 mhos respectively. The molar conductivity of salt BA at infinite dilution is_____________ .
(a) 90 mhos.cm2
(b) 110 mhos.cm2.mol-1
(c) 200 mhos.cm2.mol-1
(d) 400 mhos.cm2.mol-1
The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.025 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity.
Define the following terms: Molar conductivity (⋀m)
In the plot of molar conductivity (∧m) vs square root of concentration (c1/2) following curves are obtained for two electrolytes A and B : 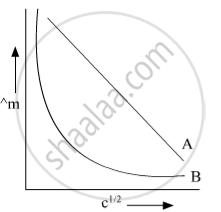
Answer the following:
(i) predict the nature of electrolytes A and B.
(ii) What happens on the extrapolation of ∧m to concentration approaching for electrolytes A and B?
In the plot of molar conductivity (∧m) vs square root of concentration (c1/2), following curves are obtained for two electrolytes A and B:
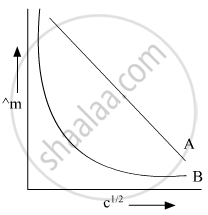
Answer the following:
(i) Predict the nature of electrolytes A and B.
(ii) What happens on extrapolation of ∧m to concentration approaching zero for electrolytes A and B?
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer.
Write the cell reaction of a lead storage battery when it is discharged. How does the density of the electrolyte change when the battery is discharged?
Assertion: Copper sulphate can be stored in zinc vessel.
Reason: Zinc is less reactive than copper.
An increase in equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to :-
Assertion (A) : Conductivity decreases with decrease in concentration of electrolyte.
Reason (R) : Number of ions per unit volume that carry the current in a solution decreases on dilution.
