Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the following terms: Molar conductivity (⋀m)
उत्तर
Molar conductivity (Λm) of a solution at a given concentration is the conductance of the volume V of the solution containing one mole of an electrolyte placed between two electrodes with the cross-sectional area (A) and the distance of unit length (l). Therefore
`^^_m=kA/l`
Since, l = 1 and A = V (volume containing one mole of electrolyte)
`^^_m=kV`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions.
The conductivity of 0.20 M solution of KCl at 298 K is 0.025 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity.
Define limiting molar conductivity.
10.0 grams of caustic soda when dissolved in 250 cm3 of water, the resultant gram molarity of solution is _______.
(A) 0.25 M
(B) 0.5 M
(C) 1.0 M
(D) 0.1 M
How can you determine limiting molar conductivity, 0 m for strong electrolyte and weak electrolyte?
In the plot of molar conductivity (∧m) vs square root of concentration (c1/2) following curves are obtained for two electrolytes A and B : 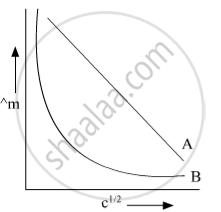
Answer the following:
(i) predict the nature of electrolytes A and B.
(ii) What happens on the extrapolation of ∧m to concentration approaching for electrolytes A and B?
Which of the following halogen acids is the strongest reducing agent?
The molar conductivity of 0.007 M acetic acid is 20 S cm2 mol−1. What is the dissociation constant of acetic acid? Choose the correct option.
`[(Λ_("H"^+)^ο = 350 "S" "cm"^2 "mol"^-1), (Λ_("CH"_3"COO"^-)^ο = 50 "S" "cm"^2 "mol"^-1)]`
The unit of molar conductivity is ______.
The solution of two electrolytes A and B are diluted. ^m of B increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Give a reason.
