Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
10.0 grams of caustic soda when dissolved in 250 cm3 of water, the resultant gram molarity of solution is _______.
(A) 0.25 M
(B) 0.5 M
(C) 1.0 M
(D) 0.1 M
उत्तर
(C) 1.0 M [1]
Molarity of NaOH solution = `10/(40xx0.25=1.0M)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The molar conductivity of cation and anion of salt BA are 180 and 220 mhos respectively. The molar conductivity of salt BA at infinite dilution is_____________ .
(a) 90 mhos.cm2
(b) 110 mhos.cm2.mol-1
(c) 200 mhos.cm2.mol-1
(d) 400 mhos.cm2.mol-1
Why conductivity of an electrolyte solution decreases with the decrease in concentration ?
The conductivity of 0.20 mol L−1 solution of KCl is 2.48 × 10−2 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation (α). Given λ0 (K+) = 73.5 S cm2 mol−1 and λ0 (C1−) = 76.5 S cm2 mol−1.
State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions.
Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution?
Define the following terms: Molar conductivity (⋀m)
Conductivity of 0.00241 M acetic acid is 7.896 × 10−5 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and if `∧_"m"^0` for acetic acid is 390.5 S cm2 mol−1, what is its dissociation constant?
Write mathematical expression of molar conductivity of the given solution at infinite dilution.
How can you determine limiting molar conductivity, 0 m for strong electrolyte and weak electrolyte?
Molar conductivity denoted by the symbol Λm is related to the conductivity of the solution by the equation (k is the conductivity and c is the concentration).
Conductivity always decreases with decrease in concentration both, for weak and strong electrolytes because of the fact that ____________.
Which of the statements about solutions of electrolytes is not correct?
\[\ce{Λ^0_m}_{(NH_4OH)}\] is equal to ______.
\[\ce{Λ^0_m H2O}\] is equal to:
(i) \[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(HCl)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaOH)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaCl)}}}}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(HNO_3)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaNO_3)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaOH)}}}}\]
(iii) \[\ce{Λ^0_{(HNO_3)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaOH)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NaNO_3)}}}}\]
(iv) \[\ce{Λ^0_m_{(NH_4OH)} + \ce{Λ^0_m_{(HCl)} - \ce{Λ^0_m_{(NH_4Cl)}}}}\]
Write the cell reaction of a lead storage battery when it is discharged. How does the density of the electrolyte change when the battery is discharged?
Assertion: Λm for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason: For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with dilution of solution.
Assertion: Copper sulphate can be stored in zinc vessel.
Reason: Zinc is less reactive than copper.
Which of the following increases with the increase in the concentration of the solution?
The molar conductance of \[\ce{NaCl, HCl}\] and \[\ce{CH3COONa}\] at infinite dilution are 126.45, 426.16 and 91.0 S cm2 mol−1 respectively. The molar conductance of \[\ce{CH3COOH}\] at infinite dilution is. Choose the right option for your answer.
The molar conductivity of 0.007 M acetic acid is 20 S cm2 mol−1. What is the dissociation constant of acetic acid? Choose the correct option.
`[(Λ_("H"^+)^ο = 350 "S" "cm"^2 "mol"^-1), (Λ_("CH"_3"COO"^-)^ο = 50 "S" "cm"^2 "mol"^-1)]`
Molar conductivity of substance “A” is 5.9 × 103 S/m and “B” is 1 × 10–16 S/m. Which of the two is most likely to be copper metal and why?
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
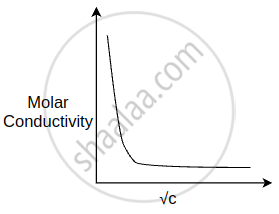
The electrolyte X is ______.
Conductivity of 2 × 10−3 M methanoic acid is 8 × 10−5 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation if `∧_"m"^0` for methanoic acid, is 404 S cm2 mol−3.
The solution of two electrolytes A and B are diluted. ^m of B increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Give a reason.
Suggest a way to determine the `∧_"m"^∘`value of water.
