Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The solution of two electrolytes A and B are diluted. ^m of B increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Give a reason.
उत्तर
B is strong because on dilution ^m increases to a little extent.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution?
Define the following terms :
Limiting molar conductivity
Match the items of Column I and Column II on the basis of data given below:
`E_("F"_2//"F"^-)^Θ` = 2.87 V, `"E"_(("Li"^(+))//("Li"^-))^Θ` = − 3.5V, `"E"_(("Au"^(3+))//("Au"))^Θ` = 1.4 V, `"E"_(("Br"_(2))//("Br"^-))^Θ` = 1.09 V
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) F2 | (a) metal is the strongest reducing agent |
| (ii) Li | (b) metal ion which is the weakest oxidising agent |
| (iii) Au3+ | (c) non metal which is the best oxidising agent |
| (iv) Br– | (d) unreactive metal |
| (v) Au | (e) anion that can be oxidised by Au3+ |
| (vi) Li+ | (f) anion which is the weakest reducing agent |
| (vii) F– | (g) metal ion which is an oxidising agent |
Assertion: Λm for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason: For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with dilution of solution.
The solubility of Co2[Fe(CN)6] in water at 25°C from the following data:
Conductivity of saturated solution of Co2[Fe(CN)6] = 2.06 × 10−6 ohm−1 cm−1 and that of water = 4.1 × 10−7 ohm−1 cm−1. The ionic molar conductivities of Co2+ and [Fe(CN)6]4− are 86 and 444 ohm−1 cm2 mol−1 respectively, is ______ × 10−6 mol/L.
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
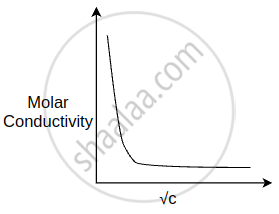
The electrolyte X is ______.
Conductivity of 2 × 10−3 M methanoic acid is 8 × 10−5 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation if `∧_"m"^0` for methanoic acid, is 404 S cm2 mol−3.
The specific conductance of 2.5 × 10-4 M formic acid is 5.25 × 10-5 ohm-1 cm-1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation.
Given `λ°_("H"^+)` = 349.5 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1 and
`λ°_("HCOO"^-) = 50.5 " ohm"^-1 "cm"^2 "mol"^-1`
Suggest a way to determine the `∧_"m"^∘`value of water.
Discuss the variation of conductivity and molar conductivity with concentration.
