Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Assertion: Λm for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason: For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with dilution of solution.
पर्याय
Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion is true but the reason is false.
Both assertion and reason are false.
Assertion is false but reason is true.
उत्तर
Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation:
Weak electrolytes dissociate partially in concentrated solution. On dilution, their degree of dissociation increases hence their Am increases sharply.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The conductivity of 0.001 mol L-1 solution of CH3COOH is 3.905× 10-5 S cm-1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation (α) Given λ°(H+)= 349.6 S cm2 mol-1 and λ°(CH3COO)= 40.9S cm2mol-1.
How can you determine limiting molar conductivity, 0 m for strong electrolyte and weak electrolyte?
Molar conductivity denoted by the symbol Λm is related to the conductivity of the solution by the equation (k is the conductivity and c is the concentration).
An increase in equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to :-
Which of the following increases with the increase in the concentration of the solution?
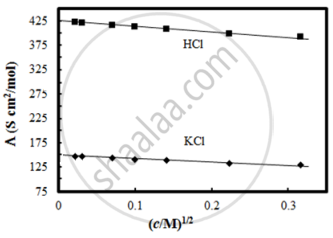
The molar conductivity of CH3COOH at infinite dilution is 390 Scm2/mol. Using the graph and given information, the molar conductivity of CH3COOK will be:
The solubility of Co2[Fe(CN)6] in water at 25°C from the following data:
Conductivity of saturated solution of Co2[Fe(CN)6] = 2.06 × 10−6 ohm−1 cm−1 and that of water = 4.1 × 10−7 ohm−1 cm−1. The ionic molar conductivities of Co2+ and [Fe(CN)6]4− are 86 and 444 ohm−1 cm2 mol−1 respectively, is ______ × 10−6 mol/L.
The variation of molar conductivity with concentration of an electrolyte (X) m aqueous solution is shown in the given figure.
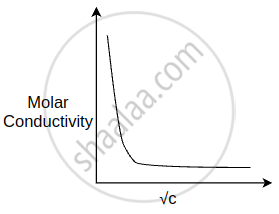
The electrolyte X is ______.
Which of the following solutions will have the highest conductivity at 298 K?
The specific conductance of 2.5 × 10-4 M formic acid is 5.25 × 10-5 ohm-1 cm-1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation.
Given `λ°_("H"^+)` = 349.5 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1 and
`λ°_("HCOO"^-) = 50.5 " ohm"^-1 "cm"^2 "mol"^-1`
