Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The molar conductivity of CH3COOH at infinite dilution is 390 Scm2/mol. Using the graph and given information, the molar conductivity of CH3COOK will be:
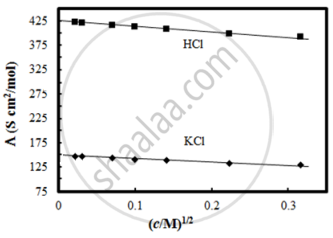
पर्याय
100 Scm2/mol
115 Scm2/mol
150 Scm2/mol
125 Scm2/mol
उत्तर
115 Scm2/mol
Explanation:
Λ°CH3COOK = Λ°CH3COOH + Λ°KCl – Λ°HCl
= 390 + 150 – 425
= 115 Scm2/mol
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the following terms: Molar conductivity (⋀m)
10.0 grams of caustic soda when dissolved in 250 cm3 of water, the resultant gram molarity of solution is _______.
(A) 0.25 M
(B) 0.5 M
(C) 1.0 M
(D) 0.1 M
The S.I. unit of cell constant for conductivity cell is __________.
\[\ce{Λ^0_m}_{(NH_4OH)}\] is equal to ______.
Molar conductivity of ionic solution depends on:
(i) temperature.
(ii) distance between electrodes.
(iii) concentration of electrolytes in solution.
(iv) surface area of electrodes.
Solutions of two electrolytes ‘A’ and ‘B’ are diluted. The Λm of ‘B’ increases 1.5 times while that of A increases 25 times. Which of the two is a strong electrolyte? Justify your answer.
Assertion: Λm for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason: For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with dilution of solution.
Molar conductivity of substance “A” is 5.9 × 103 S/m and “B” is 1 × 10–16 S/m. Which of the two is most likely to be copper metal and why?
The solubility of Co2[Fe(CN)6] in water at 25°C from the following data:
Conductivity of saturated solution of Co2[Fe(CN)6] = 2.06 × 10−6 ohm−1 cm−1 and that of water = 4.1 × 10−7 ohm−1 cm−1. The ionic molar conductivities of Co2+ and [Fe(CN)6]4− are 86 and 444 ohm−1 cm2 mol−1 respectively, is ______ × 10−6 mol/L.
Assertion (A) : Conductivity decreases with decrease in concentration of electrolyte.
Reason (R) : Number of ions per unit volume that carry the current in a solution decreases on dilution.
