Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2022-2023
Date: मार्च 2023
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions carefully.
- There are 35 questions in this question paper with internal choice.
- SECTION A consists of 18 multiple-choice questions carrying 1 mark each.
- SECTION B consists of 7 very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.
- SECTION C consists of 5 short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.
- SECTION D consists of 2 case-based questions carrying 4 marks each.
- SECTION E consists of 3 long answer questions carrying 5 marks each.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed
The major product of acid catalysed dehydration of 1-methylcyclohexanol is ______.
1-methylcyclohexane
1-methylcyclohexene
1-cyclohexylmethanol
1-methylenecyclohexane
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Which one of the following compounds is more reactive towards SN1 reaction?
CH2 = CHCH2Br
C6H5CH2Br
C6H5CH (C6H5)Br
C6H5CH(CH3) Br
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
KMnO4 is coloured due to ______.
d-d transitions
charge transfer from ligand to metal
unpaired electrons in d orbital of Mn
charge transfer from metal to ligand
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Which radioactive isotope would have the longer half-life 15O or 19O? (Given rate constants for 15O and 19O are 5.63 × 10–3 s–1 and k = 2.38 × 10–2 s–1 respectively.)
15O
19O
Both will have the same half-life
None of the above, information given is insufficient
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
The molar conductivity of CH3COOH at infinite dilution is 390 Scm2/mol. Using the graph and given information, the molar conductivity of CH3COOK will be:
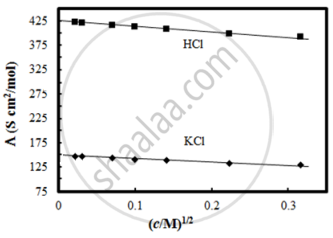
100 Scm2/mol
115 Scm2/mol
150 Scm2/mol
125 Scm2/mol
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
For the reaction, \[\ce{A +2B → AB2}\], the order w.r.t. reactant A is 2 and w.r.t. reactant B. What will be change in rate of reaction if the concentration of A is doubled and B is halved?
Increases four times
Decreases four times
Increases two times
No change
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling points:
A: Butanamine
B: N, N-Dimethylethanamine
C: N- Etthylethanaminamine
C < B < A
A < B < C
A < C < B
B < C < A
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
The CFSE of [CoCl6]3– is 18000 cm–1 the CFSE for [CoCl4]– will be ______.
18000 cm–1
8000 cm–1
2000 cm–1
16000 cm–1
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
What would be the major product of the following reaction?
\[\ce{C6H5 - CH2 - OC6H5 + HBr -> A + B}\]
A = C6H5CH2OH, B = C6H6
A = C6H5CH2OH, B = C6H5Br
A = C6H5CH3, B = C6H5Br
A = C6H5CH2Br, B = C6H5OH
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Which of the following statements is not correct for amines?
Most alkyl amines are more basic than ammonia solution.
pKb value of ethylamine is lower than benzylamine.
CH3NH2 on reaction with nitrous acid releases NO2 gas.
Hinsberg’s reagent reacts with secondary amines to form sulphonamides.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Which of the following tests/reactions is given by aldehydes as well as ketones?
Fehling’s test
Tollen’s test
2, 4 DNP test
Cannizzaro reaction
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Arrhenius equation can be represented graphically as follows:

The (i) intercept and (ii) slope of the graph are:
(i) ln A (ii) Ea/R
(i) A (ii) Ea
(i) ln A (ii) - Ea/R
(i) A (ii) - Ea
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
The number of ions formed on dissolving one molecule of FeSO4.(NH4)2SO4.6H2O in water is ______.
3
4
5
6
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
The oxidation of toluene to benzaldehyde by chromyl chloride is called ______.
Etard reaction
Riemer-Tiemann reaction
Stephen’s reaction
Cannizzaro’s reaction
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): An ether is more volatile than an alcohol of comparable molecular mass
Reason (R): Ethers are polar in nature.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures viz alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheet structure.
Reason (R): The secondary structure of proteins is stabilized by hydrogen bonding.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion: Magnetic moment values of actinides are lesser than the theoretically predicted values.
Reason: Actinide elements are strongly paramagnetic.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Tertiary amines are more basic than corresponding secondary and primary amines in gaseous state.
Reason (R): Tertiary amines have three alkyl groups which cause +I effect.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
A first-order reaction takes 69.3 min for 50% completion. What is the time needed for 80% of the reaction to get completed? (Given: log 5 = 0.6990, log 8 = 0.9030, log 2 = 0.3010)
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Account for the following:
There are 5 OH groups in glucose
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Account for the following:
Glucose is a reducing sugar
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Account for the following:
What happens when D – glucose is treated with the following reagents
Bromine water
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Account for the following:
What happens when D – glucose is treated with the following reagents
HNO3
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Advertisements
Give reason for the following:
During the electrophilic substitution reaction of haloarenes, para-substituted derivative is the major product.
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Give reason for the following:
The product formed during SN1 reaction is a racemic mixture.
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Name the suitable alcohol and reagent, from which 2-Chloro-2-methyl propane can be prepared.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Out of the Chloromethane and Fluoromethane, which one is has higher dipole moment and why?
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
The formula Co(NH3)5CO3Cl could represent a carbonate or a chloride. Write the structures and names of possible isomers.
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Corrosion is an electrochemical phenomenon. The oxygen in moist air reacts as follows:
\[\ce{O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e^{-} -> 4OH^{-}(aq)}\]
Write down the possible reactions for corrosion of zinc occurring at anode, cathode, and overall reaction to form a white layer of zinc hydroxide.
Chapter:
Explain how and why will the rate of reaction for a given reaction be affected when a catalyst is added.
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Explain how and why will the rate of reaction for a given reaction be affected when the temperature at which the reaction was taking place is decreased.
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Write the reaction and IUPAC name of the product formed when 2-Methylpropanal (isobutyraldehyde) is treated with ethyl magnesium bromide followed by hydrolysis.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Write the equations for the following reaction:
Salicylic acid is treated with acetic anhydride in the presence of conc H2SO4
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Write the equations for the following reaction:
Tert butyl chloride is treated with sodium ethoxide.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write the equations for the following reaction:
Phenol is treated with chloroform in the presence of NaOH
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Using Valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the paramagnetic complex [Mn(CN)6]3-
- type of hybridization
- magnetic moment value
- type of complex – inner, outer orbital complex
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
State Henry’s law and explain why are the tanks used by scuba divers filled with air diluted with helium (11.7% helium, 56.2% nitrogen and 32.1% oxygen)?
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Assume that argon exerts a partial pressure of 6 bar. Calculate the solubility of argon gas in water. (Given Henry’s law constant for argon dissolved in water, KH = 40 k bar)
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Give reasons for the following observation:
Aniline is acetylated before nitration reaction.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reasons for the following observation:
pKb of aniline is lower than the m-nitroaniline.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reasons for the following observation:
Primary amine on treatment with benzenesulphonyl chloride forms a product which is soluble in NaOH however secondary amine gives product which is insoluble in NaOH.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reasons for the following observation:
Aniline does not react with methyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 catalyst.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Advertisements
Identify the major product formed when 2-cyclohexylchloroethane undergoes a dehydrohalogenation reaction. Name the reagent which is used to carry out the reaction.
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Why are haloalkanes more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions than haloarenes and vinylic halides?
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Name the possible alkenes which will yield 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane on their reaction with HCl. Write the reactions involved.
Chapter:
Allyl chloride is hydrolysed more readily than n-propyl chloride. Why?
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
|
Strengthening the Foundation: Chargaff Formulates His "Rules" Many people believe that James Watson and Francis Crick discovered DNA in the 1950s. In reality, this is not the case. Rather, DNA was first identified in the late 1860s by Swiss chemist Friedrich Miescher. Then, in the decades following Miescher's discovery, other scientists- notably, Phoebus Levene and Erwin Chargaff- carried out a series of research efforts that revealed additional details about the DNA molecule, including its primary chemical components and the ways in which they joined with one another. Without the scientific foundation provided by these pioneers, Watson and Crick may never have reached their groundbreaking conclusion of 1953: that the DNA molecule exists in the form of a three-dimensional double helix. |
Answer the following questions:
- A segment of DNA has 100 adenine and 150 cytosine bases. What is the total number of nucleotides present in this segment of DNA?
- A sample of hair and blood was found at two sites. Scientists claim that the samples belong to same species. How did the scientists arrive at this conclusion?
- The sample of a virus was tested and it was found to contain 20% adenine, 20% thymine, 20% guanine and the rest cytosine. Is the genetic material of this virus (a) DNA-double helix (b) DNA-single helix (c) RNA? What do you infer from this data?
OR
How can Chargaff’s rule be used to infer that the genetic material of an organism is double-helix or single-helix?
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
| Henna is investigating the melting point of different salt solutions. She makes a salt solution using 10 mL of water with a known mass of NaCl salt. She puts the salt solution into a freezer and leaves it to freeze. She takes the frozen salt solution out of the freezer and measures the temperature when the frozen salt solution melts. She repeats each experiment. |
| S.No | Mass of the salt used in g |
Melting point in °C | |
| Readings Set 1 | Reading Set 2 | ||
| 1 | 0.3 | -1.9 | -1.9 |
| 2 | 0.4 | -2.5 | -2.6 |
| 3 | 0.5 | -3.0 | -5.5 |
| 4 | 0.6 | -3.8 | -3.8 |
| 5 | 0.8 | -5.1 | -5.0 |
| 6 | 1.0 | -6.4 | -6.3 |
Assuming the melting point of pure water as 0°C, answer the following questions:
- One temperature in the second set of results does not fit the pattern. Which temperature is that? Justify your answer.
- Why did Henna collect two sets of results?
- In place of NaCl, if Henna had used glucose, what would have been the melting point of the solution with 0.6 g glucose in it?
OR
What is the predicted melting point if 1.2 g of salt is added to 10 mL of water? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Why does the cell voltage of a mercury cell remain constant during its lifetime?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Write the reaction occurring at anode and cathode and the products of electrolysis of aq KCl.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
What is the pH of HCl solution when the hydrogen gas electrode shows a potential of −0.59 V at standard temperature and pressure?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Molar conductivity of substance “A” is 5.9 × 103 S/m and “B” is 1 × 10–16 S/m. Which of the two is most likely to be copper metal and why?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
What is the quantity of electricity in Coulombs required to produce 4.8 g of Mg from molten MgCl2? How much Ca will be produced if the same amount of electricity was passed through molten CaCl2? (Atomic mass of Mg = 24 u, atomic mass of Ca = 40 u).
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
What is the standard free energy change for the following reaction at room temperature? Is the reaction spontaneous?
\[\ce{Sn(s) + 2Cu^{2+}(aq) -> Sn^{2+}(aq) + 2Cu+(s)}\]
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
A hydrocarbon (A) with molecular formula C5H10 on ozonolysis gives two products (B) and (C). Both (B) and (C) give a yellow precipitate when heated with iodine in presence of NaOH while only (B) give a silver mirror on reaction with Tollen’s reagent.
- Identify (A), (B) and (C).
- Write the reaction of B with Tollen’s reagent.
- Write the equation for iodoform test for C.
- Write down the equation for aldol condensation reaction of B and C.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
An organic compound (A) with molecular formula C2Cl3O2H is obtained when (B) reacts with Red P and Cl2. The organic compound (B) can be obtained on the reaction of methyl magnesium chloride with dry ice followed by acid hydrolysis.
- Identify A and B.
- Write down the reaction for the formation of A from B. What is this reaction called?
- Give any one method by which organic compound B can be prepared from its corresponding acid chloride.
- Which will be the more acidic compound (A) or (B)? Why?
- Write down the reaction to prepare methane from the compound (B).
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Why are all copper halides known except that copper iodide?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Why is the `"E"_(("V"^(3+)//"V"^(2+)))^"o"` value for vanadium comparatively low?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Why \[\ce{HCl}\] should not be used for potassium permanganate titrations?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Explain the observation, at the end of each period, there is a slight increase in the atomic radius of d-block elements.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
What is the effect of pH on dichromate ion solution?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry with solutions 2022 - 2023
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2023 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
