Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give reason for the following:
The product formed during SN1 reaction is a racemic mixture.
उत्तर
During the SN1 mechanism, intermediate carbocation formed is sp2 hybridized and planar in nature. This allows the attack of nucleophiles from either side of the plane resulting in a racemic mixture.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in the presence of alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products. Explain.
What happens when chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis?
Given reasons: The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide
alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide.
Which of the following is a primary halide?
Which of the following compound will undergo racemisation when reacts with aq. KOH?
(i)
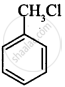
(ii)
CH3CH2CH2Cl
(iii)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2Cl}
\end{array}\]
(iv)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\ce{CH3-C-Cl}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{C2H5}
\end{array}\]
Identify the product in the following reaction: 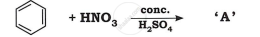
Acetic anhydride from acetic acid
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of methyl bromide.
Explain why Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
