Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What happens when chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis?
उत्तर
Chlorobenzene does not undergo hydrolysis under normal conditions. However, it undergoes hydrolysis when heated in an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at a temperature of 623 K and a pressure of 300 atm to form phenol.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which would undergo SN1 reaction faster in the following pair and why?
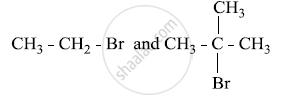
Write the main products when methyl chloride is treated with AgCN.
In the following pair of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes a faster SN1 reaction?
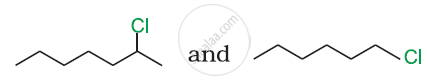
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2OH + SOCl2 ->}\]
The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in the presence of alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products. Explain.
Given reasons: The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide:
silver acetate
Which compound in the following pair reacts faster in SN2 reaction with OH–?
- CH3Br or CH3
- CH3Cl, (CH3)3CCl
Halogenation of alkanes is ____________.
SN2 mechanism proceeds through intervention of ____________.
Tertiary alkyl halides are practically inert to substitution by SN2 mechanism because of ____________.
Identify the end product (C) in the following sequence:
\[\ce{C2H5OH ->[SOCl2][Pyridine] A ->[KCN {(alc.)}] B ->[2H2O/H^+] C}\]
The increasing order of reactivity towards SN1 mechanism is:
(I) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2-CH3}\\
|\phantom{........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
(II) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(III) P–CH3O–C6H4–CH2Cl
Cyanide ion acts as an ambident nucleophile. From which end it acts as a stronger nucleophile in aqueous medium? Give reason for your answer.
Which of the following is the definition of chirality?
Give reason for the following:
The product formed during SN1 reaction is a racemic mixture.
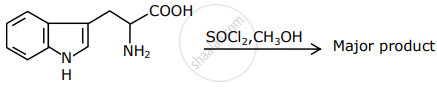
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
Optical activity of an enantiomeric mixture is +12.6° and the specific rotation of (+) isomer is +30°. The optical purity is ______ %.
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of methyl bromide.
