Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the main products when methyl chloride is treated with AgCN.
उत्तर
When methyl chloride is treated with AgCN, methyl cyanide is formed.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How do you convert the following:
Ethanol to propanenitrile
Out of C6H5CH2Cl and C6H5CHClC6H5, which is more easily hydrolysed by aqueous KOH.
The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in the presence of alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products. Explain.
The stability order for carbocation is _______.
(A) 2° > 3° > 1°
(B) 3° > 2° > 1°
(C) 3° > 1° > 2°
(D) 1° > 3° > 2°
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide:
silver acetate
AgCN reacts with haloalkanes to form isocyanide. Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as the main product. Why?
Which of the following is a chiral compound?
The increasing order of reactivity towards SN1 mechanism is:
(I) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2-CH3}\\
|\phantom{........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
(II) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(III) P–CH3O–C6H4–CH2Cl
Match the reactions given in Column I with the types of reactions given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) | 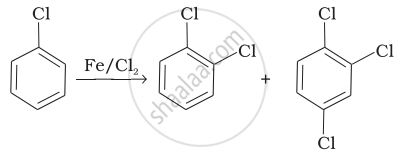 |
(a) Nucleophilic aromatic substitution |
| (ii) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - CH = CH2 + HBr -> CH3 - CH - CH3}\\ \phantom{............................}|\phantom{}\\ \phantom{.............................}\ce{Br}\phantom{} \end{array}\] |
(b) Electrophilic aromatic substitution |
| (iii) | 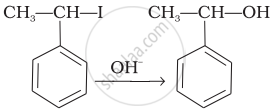 |
(c) Saytzeff elimination |
| (iv) | 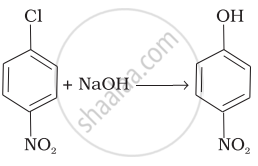 |
(d) Electrophilic addition |
| (v) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 CH2 CH CH3 ->[alc.KOH] CH3 CH = CH CH3}\\ \phantom{}|\phantom{..........................}\\ \phantom{}\ce{Br}\phantom{........................} \end{array}\] |
(e) Nucleophilic substitution (SN1) |
Explain why Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
