Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which would undergo SN1 reaction faster in the following pair and why?
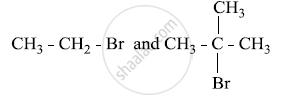
उत्तर १
Carbocations are the intermediates in the SN1 reaction. Greater the stability of the carbocations, more easily will the product be formed and hence faster will be the rate of the reaction. Because the stability of the carbocations decreases in the order: 3° carbocation > 2° carbocation > 1° carbocation > CH3+.
Therefore, the reactivity of alkyl halides towards SN1 reactions decreases in the same order, i.e. 3° alkyl halides > 2° alkyl halides > 1° alkyl halides > methyl halides.
The two structures are
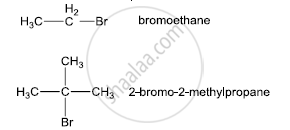
Bromoethane is a primary alkyl halide which forms a 1° carbocation intermediate in the SN1 reaction. The other compound is 2-bromo-2-methylpropane which is a tertiary alkyl halide which forms a tertiary carbocation intermediate in the SN1 reaction. Hence, 2-bromo-2-methylpropane undergoes an SN1 reaction faster than bromoethane
उत्तर २
A tertiary alkyl halide tends to undergo the SN1 mechanism because it can form a tertiary carbocation, which is stabilised by the three alkyl groups attached to it. As alkyl groups are electron donating, they allow the positive charge in the carbocation to be delocalised by the induction effect. Hence, out of the given pairs, (CH3)3C-Br would undergo SN1 reaction faster than CH3-CH2-Br.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given reasons: C–Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than C–Cl bond length in CH3–Cl.
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide
alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide.
AgCN reacts with haloalkanes to form isocyanide. Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as the main product. Why?
Optically active isomers but not mirror images are called ____________.
SN1 reaction of alkyl halides lead to ___________.
Identify the end product (C) in the following sequence:
\[\ce{C2H5OH ->[SOCl2][Pyridine] A ->[KCN {(alc.)}] B ->[2H2O/H^+] C}\]
Which of the following compound will undergo racemisation when reacts with aq. KOH?
(i)
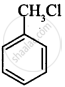
(ii)
CH3CH2CH2Cl
(iii)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2Cl}
\end{array}\]
(iv)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\ce{CH3-C-Cl}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{C2H5}
\end{array}\]
Elimination reactions (especially β-elimination) are as common as the nucleophilic substitution reaction in case of alkyl halides. Specify the reagents used in both cases.
Identify the product in the following reaction: 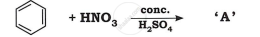
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of methyl bromide.
