Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Elimination reactions (especially β-elimination) are as common as the nucleophilic substitution reaction in case of alkyl halides. Specify the reagents used in both cases.
उत्तर
Alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution as well as elimination (Beta-elimination) reaction. However, by proper choice of reagents and reaction conditions, a particular product can be obtained. Usually strong and bulky bases and high temperature favour elimination reactions while weaker and smaller bases and lower temperature favour substitution reactions. For example, ethyl bromide on heating with alcoholic KOH (which contain stronger base,
Nucleophilic substitution: Reagents used nucleophilies like
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give reasons for the following:
(CH3)3C–O–CH3 on reaction with HI gives (CH3)3C–I and CH3–OH as the main products and not (CH3)3C–OH and CH3–I.
Which alkyl halide from the following pair would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism? Explain your answer.
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br or
Out of C6H5CH2Cl and C6H5CHClC6H5, which is more easily hydrolysed by aqueous KOH.
Which among MeX, RCH2X, R2CHX and R3CX is most reactive towards SN2 reaction?
Which of the following compounds is optically active?
Racemic compound has ____________.
A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo ______.
How do polar solvents help in the first step in SN1 mechanism?
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution. Predict and explain the order of reactivity of the following compounds towards nucleophilic substitution:
| (I) | 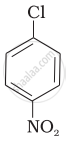 |
| (II) | 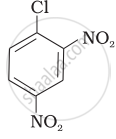 |
| (III) | 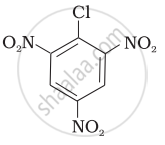 |
Which of the following is the definition of chirality?
