Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Elimination reactions (especially β-elimination) are as common as the nucleophilic substitution reaction in case of alkyl halides. Specify the reagents used in both cases.
Solution
Alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution as well as elimination (Beta-elimination) reaction. However, by proper choice of reagents and reaction conditions, a particular product can be obtained. Usually strong and bulky bases and high temperature favour elimination reactions while weaker and smaller bases and lower temperature favour substitution reactions. For example, ethyl bromide on heating with alcoholic KOH (which contain stronger base, \[\ce{C2H5O}\] ion) at about 473-523 K undergoes elimination to give ethene. But with aqueous \[\ce{KOH}\] at about 373 K, it gives ethanol.
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br ->[alc.KOH][473-523 K] CH2 = CH2 (Elimination)}\]
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br ->[aq.KOH][373 K] CH3CH2OH (Substitution)}\]
Nucleophilic substitution: Reagents used nucleophilies like \[\ce{- \overset{-}{O}H, NH3, \overset{-}{C} ≡ N;, AgCN:, O = N - O, \overset{-}{O}R}\]' etc. also, alc. \[\ce{KOH}\] at lower temperature (373 K) undergoes substitution reaction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the structures of A, B and C in the following:

The stability order for carbocation is _______.
(A) 2° > 3° > 1°
(B) 3° > 2° > 1°
(C) 3° > 1° > 2°
(D) 1° > 3° > 2°
Given reasons: The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
Which one of the following halogen compounds is difficult to be hydrolysed by SN1 mechanism?
Which of the following compounds is optically active?
An organic molecule necessarily shows optical activity if it ____________.
The increasing order of reactivity towards SN1 mechanism is:
(I) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2-CH3}\\
|\phantom{........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
(II) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(III) P–CH3O–C6H4–CH2Cl
Which of the following statements are correct about this reaction?
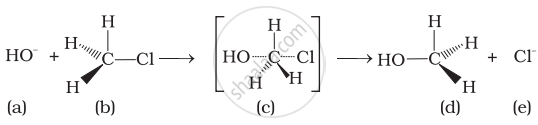
(i) The given reaction follows SN2 mechanism.
(ii) (b) and (d) have opposite configuration.
(iii) (b) and (d) have same configuration.
(iv) The given reaction follows SN1 mechanism.
CCl4 is insoluble in water because:-
Among the following compounds I - IV, which one forms a yellow precipitate on reacting sequentially with (i) NaOH (ii) dil. HNO3 (iii) AgNO3?
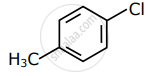 |
 |
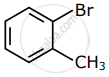 |
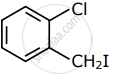 |
| I | II | III | IV |
