Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Elimination reactions (especially β-elimination) are as common as the nucleophilic substitution reaction in case of alkyl halides. Specify the reagents used in both cases.
उत्तर
Alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution as well as elimination (Beta-elimination) reaction. However, by proper choice of reagents and reaction conditions, a particular product can be obtained. Usually strong and bulky bases and high temperature favour elimination reactions while weaker and smaller bases and lower temperature favour substitution reactions. For example, ethyl bromide on heating with alcoholic KOH (which contain stronger base, \[\ce{C2H5O}\] ion) at about 473-523 K undergoes elimination to give ethene. But with aqueous \[\ce{KOH}\] at about 373 K, it gives ethanol.
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br ->[alc.KOH][473-523 K] CH2 = CH2 (Elimination)}\]
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br ->[aq.KOH][373 K] CH3CH2OH (Substitution)}\]
Nucleophilic substitution: Reagents used nucleophilies like \[\ce{- \overset{-}{O}H, NH3, \overset{-}{C} ≡ N;, AgCN:, O = N - O, \overset{-}{O}R}\]' etc. also, alc. \[\ce{KOH}\] at lower temperature (373 K) undergoes substitution reaction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of bromomethane.
Write the major products(s) in the following:
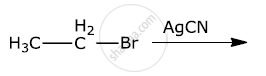
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br + KCN ->[aq.ethanol]}\]
What happens when ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH?
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Ethyl chloride to propanoic acid
C–Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than C–Cl bond length in CH3–Cl.
AgCN reacts with haloalkanes to form isocyanide. Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as the main product. Why?
The reaction of C6H5–CH=CH–CH3 with HBr produces:
Which of the following compounds will give a racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by OH ion?
1-Bromoethane, 1-Bromopropane, 1-Bromobutane, Bromobenzene
Optical activity of an enantiomeric mixture is +12.6° and the specific rotation of (+) isomer is +30°. The optical purity is ______ %.
