Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution. Predict and explain the order of reactivity of the following compounds towards nucleophilic substitution:
| (I) | 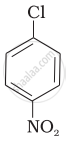 |
| (II) | 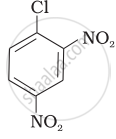 |
| (III) | 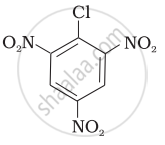 |
उत्तर
After the attachment of the nucleophile at the carbon carrying -Cl, the intermediate compound is stabilised due to resonance. Due to electron-withdrawing nature of-NO2, the nucleophile is easily attached to the benzene ring. Greater the number of -NO2 groups in the molecule, greater will be the ease with which the nucleophile will be attached. Hence, the order of reactivity is III > II > I.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of bromomethane.
Write the isomers of the compound having the formula C4H9Br.
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br + KCN ->[aq.ethanol]}\]
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2OH + SOCl2 ->}\]
Arrange the compounds of the following set in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
1-Bromobutane, 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane, 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane
The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in the presence of alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products. Explain.
What happens when chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis?
Optically active isomers but not mirror images are called ____________.
Which of the following statements are correct about this reaction?
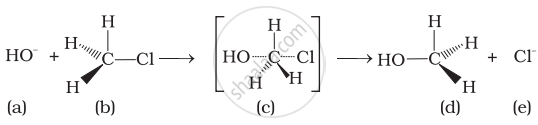
(i) The given reaction follows SN2 mechanism.
(ii) (b) and (d) have opposite configuration.
(iii) (b) and (d) have same configuration.
(iv) The given reaction follows SN1 mechanism.
Convert bromoethane to propanamine.
