Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br + KCN ->[aq.ethanol]}\]
उत्तर
\[\ce{\underset{Bromoethane}{CH3CH2Br} + KCN ->[aq.ethanol][(nucleophilic substitution)] \underset{Propanenitrile}{CH3CH2CN} + KBr}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which would undergo SN1 reaction faster in the following pair and why?
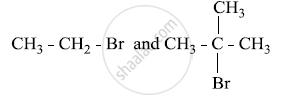
Which alkyl halide from the following pair would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism? Explain your answer.
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br or \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3CH2CHCH3}\\
\phantom{...}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{Br}\
\end{array}\]
Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
\[\ce{{n}BuBr + KCN ->[EtOH-H2O] {n}BuCN}\]
Arrange the compounds of the following set in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
1-Bromobutane, 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane, 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane
What happens when chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis?
Answer the following question.
Write one stereochemical difference between SN1 and SN2 reactions.
The process of separation of a racemic modification into d and l-enantiomers is called ____________.
Which of the following compounds is optically active?
SN1 reaction of alkyl halides lead to ___________.
Identify the end product (C) in the following sequence:
\[\ce{C2H5OH ->[SOCl2][Pyridine] A ->[KCN {(alc.)}] B ->[2H2O/H^+] C}\]
Which of the following statements are correct about the kinetics of this reaction?
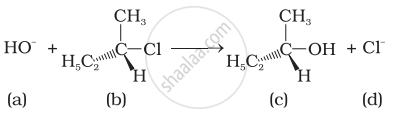
(i) The rate of reaction depends on the concentration of only (b).
(ii) The rate of reaction depends on concentration of both (a) and (b).
(iii) Molecularity of reaction is one.
(iv) Molecularity of reaction is two.
Compound ‘A’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C4H9Br}\] is treated with aq. \[\ce{KOH}\] solution. The rate of this reaction depends upon the concentration of the compound ‘A’ only. When another optically active isomer ‘B’ of this compound was treated with aq. \[\ce{KOH}\] solution, the rate of reaction was found to be dependent on concentration of compound and \[\ce{KOH}\] both.
(i) Write down the structural formula of both compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’.
(ii) Out of these two compounds, which one will be converted to the product with inverted configuration.
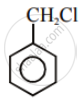
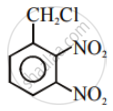
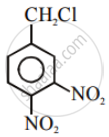
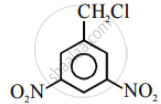
Write the structures and names of the compounds formed when compound ‘A’ with molecular formula, \[\ce{C7H8}\] is treated with \[\ce{Cl2}\] in the presence of \[\ce{FeCl3}\].
Match the reactions given in Column I with the types of reactions given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) | 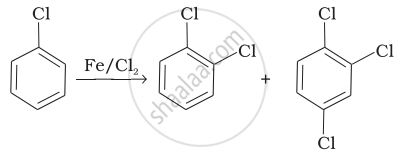 |
(a) Nucleophilic aromatic substitution |
| (ii) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - CH = CH2 + HBr -> CH3 - CH - CH3}\\ \phantom{............................}|\phantom{}\\ \phantom{.............................}\ce{Br}\phantom{} \end{array}\] |
(b) Electrophilic aromatic substitution |
| (iii) | 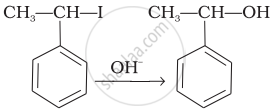 |
(c) Saytzeff elimination |
| (iv) | 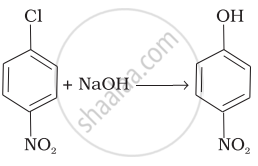 |
(d) Electrophilic addition |
| (v) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 CH2 CH CH3 ->[alc.KOH] CH3 CH = CH CH3}\\ \phantom{}|\phantom{..........................}\\ \phantom{}\ce{Br}\phantom{........................} \end{array}\] |
(e) Nucleophilic substitution (SN1) |
When CH3CH2CHCl2 is treated NaNH2 product formed is:-
CCl4 is insoluble in water because:-
The decreasing order of reactivity of the following compounds towards nucleophilic substitution (SN2) is ______.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of reactivity towards SN2 reaction.
2-Bromopentane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of methyl bromide.