Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
\[\ce{{n}BuBr + KCN ->[EtOH-H2O] {n}BuCN}\]
उत्तर १
This reaction is a first-order nucleophilic substitution (SN1). The mechanism can be stated as:
Step 1: Generation of nucleophile:
\[\ce{KCN ->[EtOH-H2O]K+ + \overset{—}{C} ≡ N}\]
Step 2: Nucleophilic attack and formation of transition state:
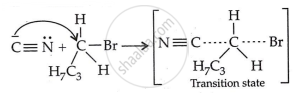
Step 3: Generation of product:
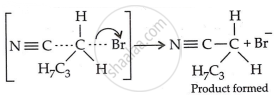
Therefore, we have
\[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - Br + KCN ->[EtOH/H2O]CH3CH2CH2CH2CN + KBr}\]
उत्तर २
KCN is the resonating hybrid of the following structures:
\[\ce{K^+ [^- :C ≡ N: ↔ :C = \overset{\bullet\bullet}{N} :^-]}\]
Therefore, CN⁻ acts as an ambident nucleophile. It can attack the carbon atom of the C-Br bond in n-BuBr through either the carbon (C) or nitrogen (N) atom. Since the C-N bond is weaker than the C-C bond, the attack occurs at the carbon atom, leading to the formation of n-butyl cyanide.
\[\ce{K^+CN^- + \underset{n-butyl bromide}{CH3CH2CH2\overset{δ+}{C}H2 - \overset{δ-}{B}r} -> \underset{n-butyl cyanide}{CH3CH2CH2CH2CN} + KBr}\]
Notes
Students can refer to the provided solutions based on their preferred marks.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How do you convert the following:
Ethanol to propanenitrile
Write the structure of the major product in each of the following reaction :
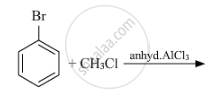
Write the isomers of the compound having the formula C4H9Br.
What are ambident nucleophiles? Explain with an example.
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH(Br)CH2CH3 + NaOH ->[water]}\]
Arrange the compounds of the following set in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
1-Bromobutane, 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane, 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane
What happens when chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis?
Given reasons: The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
Given reasons: SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemization in optically active alkyl halides.
The order of reactivity of the given haloalkanes towards nucleophile is:
Isopropyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis by:
An important chemical method to resolve a racemic mixture makes use of the formation of ______.
Among the following, the dissociation constant is highest for:
SN1 reaction of alkyl halides lead to ___________.
The increasing order of reactivity towards SN1 mechanism is:
(I) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2-CH3}\\
|\phantom{........}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
(II) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(III) P–CH3O–C6H4–CH2Cl
Ethylene chloride and ethylidene chloride are isomers. Identify the correct statements.
(i) Both the compounds form same product on treatment with alcoholic KOH.
(ii) Both the compounds form same product on treatment with aq.NaOH.
(iii) Both the compounds form same product on reduction.
(iv) Both the compounds are optically active.
Which of the compounds will react faster in SN1 reaction with the –OH ion?
\[\ce{CH3-CH2-Cl}\] or \[\ce{C6H5-CH2-Cl}\]
Inversion of configuration occurs in ______.
Explain why Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
