Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH(Br)CH2CH3 + NaOH ->[water]}\]
उत्तर
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH2CH3 + NaOH ->[H2O][Hydrolysis] CH3 - CH - CH2CH3 + NaBr + H2O}\\
|\phantom{........................................}|\phantom{......................}\\
\ce{\underset{2-Bromobutane}{Br}}\phantom{................................}\ce{\underset{Butan-2-ol}{OH}}\phantom{......................}
\end{array}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the structure of an isomer of compound C4H9Br which is most reactive towards SN1 reaction
Which would undergo SN1 reaction faster in the following pair and why?
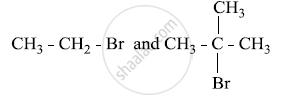
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Toluene to benzyl alcohol
SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemization in optically active alkyl halides.
The stability order for carbocation is _______.
(A) 2° > 3° > 1°
(B) 3° > 2° > 1°
(C) 3° > 1° > 2°
(D) 1° > 3° > 2°
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide
alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide.
AgCN reacts with haloalkanes to form isocyanide. Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as the main product. Why?
SN2 mechanism proceeds through intervention of ____________.
Which of the following is an optically active compound?
The correct order of increasing the reactivity of C–X bond towards nucleophile in following compounds.
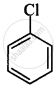
(I)
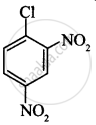
(II)
(CH3)3CCl
(III)
(CH3)2CHCl
(IV)
Which of the following compound will undergo racemisation when reacts with aq. KOH?
(i)
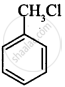
(ii)
CH3CH2CH2Cl
(iii)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2Cl}
\end{array}\]
(iv)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\ce{CH3-C-Cl}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{C2H5}
\end{array}\]
Which of the following alkyl halides will undergo SN1 reaction most readily?
Ethylene chloride and ethylidene chloride are isomers. Identify the correct statements.
(i) Both the compounds form same product on treatment with alcoholic KOH.
(ii) Both the compounds form same product on treatment with aq.NaOH.
(iii) Both the compounds form same product on reduction.
(iv) Both the compounds are optically active.
Write the structures and names of the compounds formed when compound ‘A’ with molecular formula, \[\ce{C7H8}\] is treated with \[\ce{Cl2}\] in the presence of \[\ce{FeCl3}\].
Cyanide ion acts as an ambident nucleophile. From which end it acts as a stronger nucleophile in aqueous medium? Give reason for your answer.
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
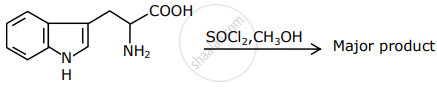
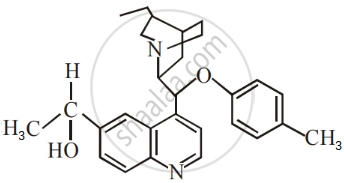
The number of chiral carbons present in the molecule given below is ______.
Optical activity of an enantiomeric mixture is +12.6° and the specific rotation of (+) isomer is +30°. The optical purity is ______ %.
Inversion of configuration occurs in ______.
Explain why Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
