Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given reasons: SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemization in optically active alkyl halides.
उत्तर
In SN1 reaction, formation of carbocation as an intermediate takes place. This carbocation has sp2-hybridised and planar structure. This planar carbocation is attacked by nucleophile from both the sides equally to form d and l isomers in equal proportion. Such products are called racemic mixture. Hence, SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemisation in optically active alkyl halides.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which alkyl halide from the following pair would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism? Explain your answer.
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br or \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3CH2CHCH3}\\
\phantom{...}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{Br}\
\end{array}\]
An organic molecule necessarily shows optical activity if it ____________.
Which of the following compound will undergo racemisation when reacts with aq. KOH?
(i)
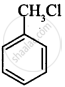
(ii)
CH3CH2CH2Cl
(iii)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2Cl}
\end{array}\]
(iv)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\ce{CH3-C-Cl}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{C2H5}
\end{array}\]
A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo ______.
Which one of the following compounds is more reactive towards SN1 reaction?
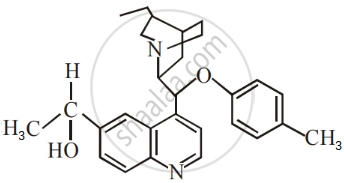
The number of chiral carbons present in the molecule given below is ______.
In SN1 reactions, the correct order of reactivity for the following compounds:
CH3Cl, CH3CH2Cl, (CH3)2CHCl and (CH3)3CCl is ______.
Racemisation occurs in ______.
An organic compound A with the molecular formula (+) C4H9Br undergoes hydrolysis to form (+) C4H9OH. Give the structure of A and write the mechanism of the reaction.
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of methyl bromide.
