Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose the second charge in the previous problem is −1.0 × 10−6 C. Locate the position where a third charge will not experience a net force.
उत्तर
Given:
\[q_1 = 2 \times {10}^{- 6} C\]
\[ q_2 = - 1 \times {10}^{- 6} C\]
Since both the charges are opposite in nature, the third charge cannot be placed between them. Let the third charge, q, be placed at a distance of x cm from charge q1, as shown in the figure.
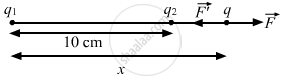
By Coulomb's Law, force,
\[F - F' = 0\]
\[\Rightarrow F = F'\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times 2 \times {10}^{- 6} \times q}{x^2} = \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times {10}^{- 6} \times q}{\left( x - 10 \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x^2 = 2 \left( x - 10 \right)^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow x^2 - 40x + 200 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 20 \pm 10\sqrt{2} \text{ m} \]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 34 . 14 \text{ cm } ( \because x \neq 20 - 10\sqrt{2})\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check that the ratio ke2/G memp is dimensionless. Look up a Table of Physical Constants and determine the value of this ratio. What does the ratio signify?
At what separation should two equal charges, 1.0 C each, be placed, so that the force between them equals the weight of a 50 kg person?
Two charges 2.0 × 10−6 C and 1.0 × 10−6 C are placed at a separation of 10 cm. Where should a third charge be placed, such that it experiences no net force due to these charges?
Two charged particles are placed 1.0 cm apart. What is the minimum possible magnitude of the electric force acting on each charge?
Suppose an attractive nuclear force acts between two protons which may be written as F=Ce−kr/r2. Write down the dimensional formulae and appropriate SI units of C and k.
Suppose an attractive nuclear force acts between two protons which may be written as F=Ce−kr/r2. Suppose that k = 1 fermi−1 and that the repulsive electric force between the protons is just balanced by the attractive nuclear force when the separation is 5 fermi. Find the value of C.
A hydrogen atom contains one proton and one electron. It may be assumed that the electron revolves in a circle of radius 0.53 angstrom (1 angstrom = 10−10 m and is abbreviated as Å ) with the proton at the centre. The hydrogen atom is said to be in the ground state in this case. Find the magnitude of the electric force between the proton and the electron of a hydrogen atom in its ground state.
Ten positively-charged particles are kept fixed on the x-axis at points x = 10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm, ...., 100 cm. the first particle has a charge 1.0 × 10−8 C, the second 8 × 10−8 C, the third 27 × 10−8 C and so on. The tenth particle has a charge 1000 × 10−8 C. Find the magnitude of the electric force acting on a 1 C charge placed at the origin.
A particle with a charge of 2.0 × 10−4 C is placed directly below and at a separation of 10 cm from the bob of a simple pendulum at rest. The mass of the bob is 100 g. What charge should the bob be given so that the string becomes loose?
Two particles A and B, each carrying a charge Q, are held fixed with a separation dbetween them. A particle C of mass m and charge q is kept at the middle point of the line AB. Under what conditions will the particle C execute simple harmonic motion if it is released after such a small displacement? Find the time period of the oscillations if these conditions are satisfied.
How much work has to be done in assembling three charged particles at the vertices of an equilateral triangle, as shown in the figure?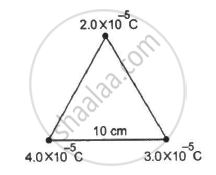
Two identical particles, each with a charge of 2.0 × 10−4 C and mass of 10 g, are kept at a separation of 10 cm and then released. What would be the speed of the particles when the separation becomes large?
Answer the following question.
What is relative permittivity?
Three charges +Q, q, +Q are placed respectively, at distance, 0, d/2 and d from the origin, on the X-axis. If the net force experienced by +Q, placed at x = 0, is zero then value of q is ____________.
A total charge Q is broken in two parts Q1 and Q2 and they are placed at a distance R from each other. The maximum force of repulsion between them will occur, when ____________.
Polarised dielectric is equivalent to ______.
Two point charges +3 µC and +8 µC repel each other with a force of 40 N. If a charge of -5 µC is added to each of them, then force between them will become ______.
The ratio of the forces between two small spheres with constant charge (a) in air (b) in a medium of dielectric constant K is ______.
A charge Q is divided into two parts of q and Q – q. If the coulomb repulsion between them when they are separated is to be maximum, the ratio of Q/q should be ______.
