Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Suppose the second charge in the previous problem is −1.0 × 10−6 C. Locate the position where a third charge will not experience a net force.
Solution
Given:
\[q_1 = 2 \times {10}^{- 6} C\]
\[ q_2 = - 1 \times {10}^{- 6} C\]
Since both the charges are opposite in nature, the third charge cannot be placed between them. Let the third charge, q, be placed at a distance of x cm from charge q1, as shown in the figure.
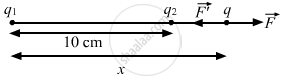
By Coulomb's Law, force,
\[F - F' = 0\]
\[\Rightarrow F = F'\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times 2 \times {10}^{- 6} \times q}{x^2} = \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times {10}^{- 6} \times q}{\left( x - 10 \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x^2 = 2 \left( x - 10 \right)^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow x^2 - 40x + 200 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 20 \pm 10\sqrt{2} \text{ m} \]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 34 . 14 \text{ cm } ( \because x \neq 20 - 10\sqrt{2})\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Check that the ratio ke2/G memp is dimensionless. Look up a Table of Physical Constants and determine the value of this ratio. What does the ratio signify?
Plot a graph showing the variation of coulomb force (F) versus ,`(1/r^2)` where r is the distance between the two charges of each pair of charges: (1 μC, 2 μC) and (2 μC, − 3 μC). Interpret the graphs obtained.
A charge of 1.0 C is placed at the top of your college building and another equal charge at the top of your house. Take the separation between the two charges to be 2.0 km. Find the force exerted by the charges on each other. How many times your weight is this force?
Two charged particles are placed 1.0 cm apart. What is the minimum possible magnitude of the electric force acting on each charge?
Two charged particles with charge 2.0 × 10−8 C each are joined by an insulating string of length 1 m and the system is kept on a smooth horizontal table. Find the tension in the string.
A particle A with a charge of 2.0 × 10−6 C and a mass of 100 g is placed at the bottom of a smooth inclined plane of inclination 30°. Where should another particle B, with the same charge and mass, be placed on the incline so that it may remain in equilibrium?
Repeat the previous problem if the particle C is displaced through a distance x along the line AB.
Two particles A and B possessing charges of +2.00 × 10−6 C and of −4.00 × 10−6 C, respectively, are held fixed at a separation of 20.0 cm. Locate the points (s) on the line AB, where (a) the electric field is zero (b) the electric potential is zero.
A water particle of mass 10.0 mg and with a charge of 1.50 × 10−6 C stays suspended in a room. What is the magnitude of electric field in the room? What is its direction ?
Two charged particles, with equal charges of 2.0 × 10−5 C, are brought from infinity to within a separation of 10 cm. Find the increase in the electric potential energy during the process
Solve numerical example.
Three equal charges of 10×10-8 C respectively, each located at the corners of a right triangle whose sides are 15 cm, 20 cm, and 25cm respectively. Find the force exerted on the charge located at the 90° angle.
A force F acts between sodium and chlorine ions of salt (sodium chloride) when put 1 cm apart in air. The permittivity of air and dielectric constant of water are `epsilon_0` and K respectively. When a piece of salt is put in water, electrical force acting between sodium and chlorine ions 1 cm apart is ____________.
The force between two charges 0.06 m apart is 5 N. If each charge is moved towards the other by 0.01 m, then the force between them will become ____________.
Two point charges +3 µC and +8 µC repel each other with a force of 40 N. If a charge of -5 µC is added to each of them, then force between them will become ______.
The ratio of the forces between two small spheres with constant charge (a) in air (b) in a medium of dielectric constant K is ______.
The unit of charge is ______.
Four equal charges q are placed at the four comers A, B, C, D of a square of length a. The magnitude of the force on the charge at B will be ______.
Two charges of equal magnitudes kept at a distance r exert a force F on each other. If the charges are halved and distance between them is doubled, then the new force acting on each charge is ______.
Two point charges +2 C and +6 C repel each other with a force of 12 N. If a charge of -4 C is given to each of these charges, then the force now is ______.
