Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The energy of an electron in the nth orbit of the hydrogen atom is En = -13.6/n2eV. The negative sign of energy indicates that ______.
पर्याय
electron is free to move.
electron is bound to the nucleus.
the kinetic energy of the electron is equal to the potential energy of the electron.
atom is radiating energy.
उत्तर
The energy of an electron in the nth orbit of the hydrogen atom is En = -13.6/n2eV. The negative sign of energy indicates that the electron is bound to the nucleus.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) State Bohr's quantization condition for defining stationary orbits. How does the de Broglie hypothesis explain the stationary orbits?
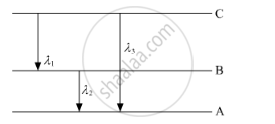
(ii) Find the relation between three wavelengths λ1, λ2 and λ3 from the energy-level diagram shown below.
The numerical value of ionization energy in eV equals the ionization potential in volts. Does the equality hold if these quantities are measured in some other units?
A neutron moving with a speed υ strikes a hydrogen atom in ground state moving towards it with the same speed. Find the minimum speed of the neutron for which inelastic (completely or partially) collision may take place. The mass of neutron = mass of hydrogen = 1.67 × 10−27 kg.v
How are various lines of Lyman series formed? Explain on the basis of Bohr’s theory.
According to Bohr's model of hydrogen atom, an electron can revolve round a proton indefinitely, if its path is ______.
When an electric discharge is passed through hydrogen gas, the hydrogen molecules dissociate to produce excited hydrogen atoms. These excited atoms emit electromagnetic radiation of discrete frequencies which can be given by the general formula
`bar(v) = 109677 1/n_1^2 - 1/n_f^2`
What points of Bohr’s model of an atom can be used to arrive at this formula? Based on these points derive the above formula giving description of each step and each term.
According to the Bohr theory of H-atom, the speed of the electron, its energy and the radius of its orbit varies with the principal quantum number n, respectively, as:
The ratio of the ionization energy of H and Be+3 is ______.
The binding energy of a H-atom, considering an electron moving around a fixed nuclei (proton), is B = `- (Me^4)/(8n^2ε_0^2h^2)`. (m = electron mass). If one decides to work in a frame of reference where the electron is at rest, the proton would be moving around it. By similar arguments, the binding energy would be
B = `- (Me^4)/(8n^2ε_0^2h^2)` (M = proton mass)
This last expression is not correct because ______.
Find the ratio of energies of photons produced due to transition of an election of hydrogen atom from its (i) second permitted energy level to the first level. and (ii) the highest permitted energy level to the first permitted level.
